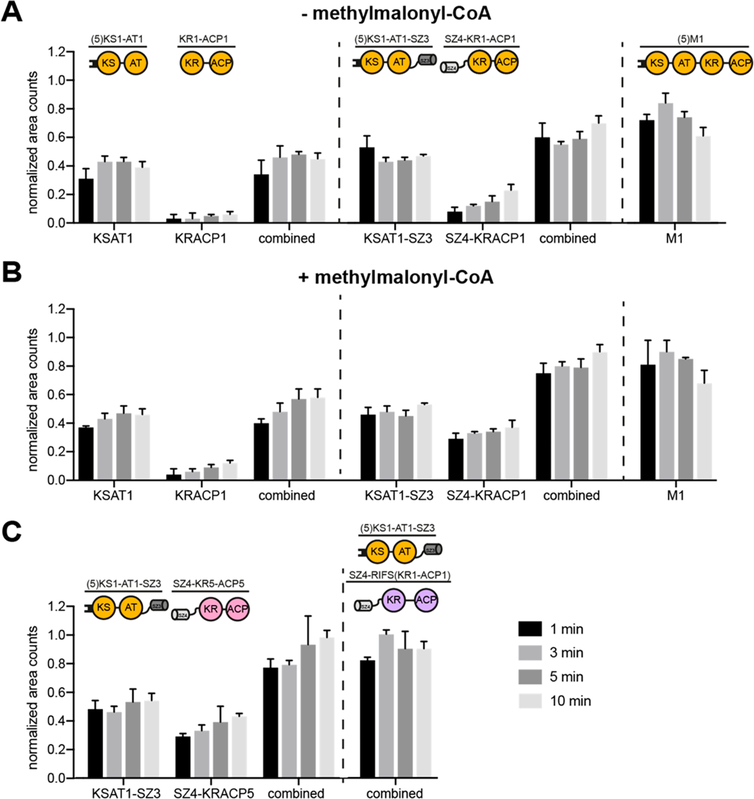
Figure 3.
Comparison of chain translocation and elongation rates of intact versus split modules. The occupancy of individual proteins by growing polyketide chain precursors was measured in the absence (A) or presence (B) of methylmalonyl-CoA, and in modules containing chimeric KS:ACP interfaces (C, with methylmalonyl-CoA). All measurements included LDD(4) plus the designated split or intact module combinations. Labeling of the different proteins was quantified at different time points (1, 3, 5, and 10 min), and the resulting counts were normalized based on the maximal occupancy. Combined counts of both the KS and ACP containing proteins are also presented for split-module systems. In the case of RIFS Module 1, the N- and C-terminal fragments could not be separated by SDS-PAGE gel; hence only combined counts are reported (panel C). All measurements were performed in triplicate using 2 μM enzyme concentration and nonlimiting concentrations of propionyl-CoA, methylmalonyl-CoA, and NADPH.