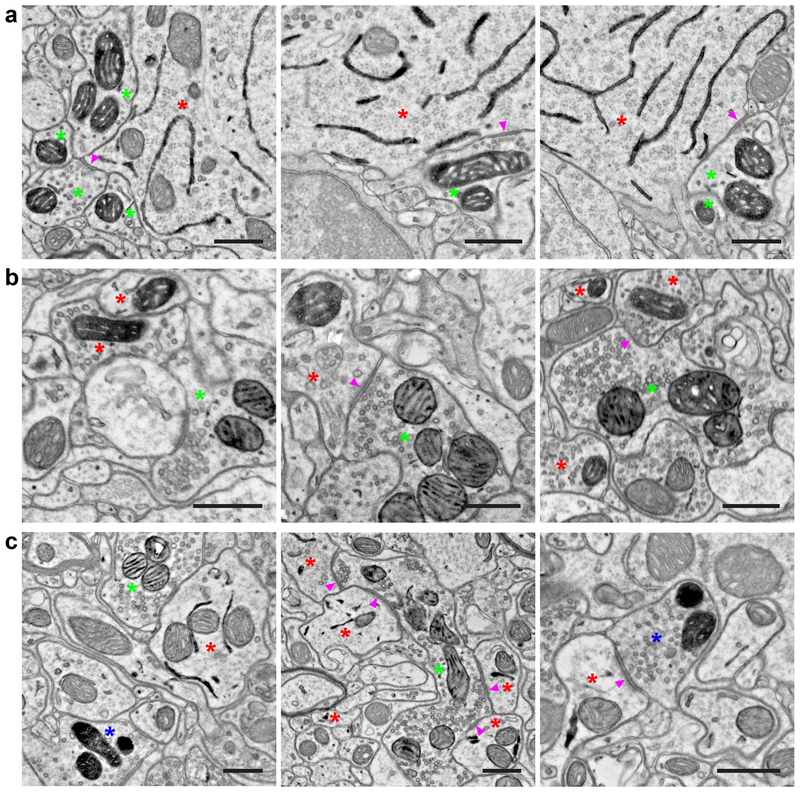
Figure 3. Double and triple EM labeling using orthogonal peroxidase reporter constructs.
(a) EM images showing double labeling of cortical layer 5 pyramidal neurons (ER) using Tg(Rbp4-Cre)KL100 and AAV1-DIO-ER-dAPEX2 (red asterisks), and fast-spiking GABAergic interneurons (mitochondrial matrix) using PvalbT2A-FlpO and AAV1-FDIO-Matrix-dAPEX2 (green asterisks). Note the symmetric perisomatic synapses made by fast-spiking interneurons onto layer 5 pyramidal neurons (arrowheads). n = 4 animals and experiments.
(b) EM images showing double labeling of spinal cord dorsal horn inhibitory interneurons (mitochondrial matrix) using Slc32a1IRES-Cre and AAV1-DIO-Matrix-dAPEX2 (red asterisks), and primary somatosensory afferents (mitochondrial IMS) using AvilFlpO and AAV9-FDIO-IMS-dAPEX2 (green asterisks). Arrowheads: an axodendritic synapse from a primary somatosensory afferent to an inhibitory interneuron (Middle) and an axoaxonic synapse from an inhibitory interneuron to a primary somatosensory afferent (Right). n = 3 animals and experiments.
(c) EM images showing triple labeling of dorsal horn inhibitory interneurons (ER) using Slc32a1IRES-Cre and AAV1-DIO-ER-dAPEX2 (red asterisks), primary somatosensory afferents (mitochondrial IMS) using AvilFlpO and AAV9-FDIO-IMS-dAPEX2 (green asterisks), and corticospinal inputs (mitochondrial matrix) using cortical injections of AAV1-Matrix-dAPEX2 (blue asterisks). (Left) All three stains can be clearly visualized and distinguished in the same field of view. (Middle) A primary somatosensory afferent making axodendritic synaptic contacts onto inhibitory interneurons (arrowheads). Note the numerous synaptic contacts made by the primary somatosensory afferent, which is characteristic of the central axons of glomeruli. (Right) A corticospinal axon making an axodendritic synapse onto an inhibitory interneuron (arrowhead). This type of simple synaptic arrangement is typical of corticospinal inputs. n = 2 animals and experiments.
Scale bars: 0.5 μm.