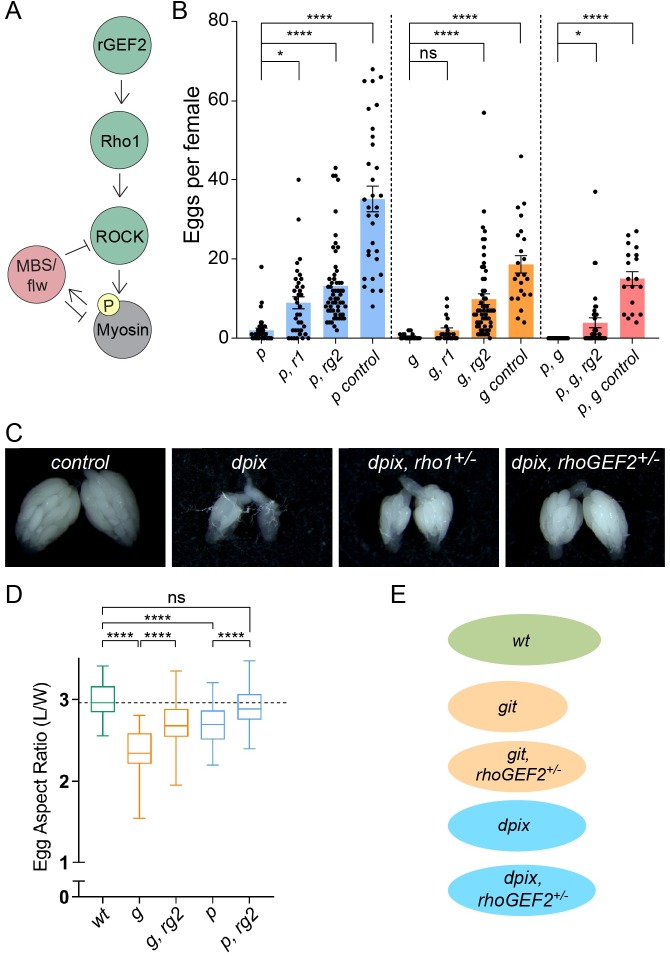
Fig 4. Reduction of myosin activators rescues egg chamber viability and tissue morphology defects in the absence of the dPix-Git complex.
(A) Schematic of signalling cascade for non-muscle myosin regulatory light chain (Myosin) phosphorylation in D. melanogaster, highlighting the role of Rho1 and RhoGEF2 (rGEF2) as canonical upstream activators of myosin. (B) Number of mature eggs produced per female for the indicated genotypes. Statistical tests are ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test. Genotype groupings considered for statistical comparison are indicated by the dashed lines in (B), and error bars are standard error of the mean. Genotypes and sample sizes as follows: (p) dpix, n = 37; (p, r1) dpix, rho1+/-, n = 36; (p, rg2) dpix, rhoGEF2+/-, n = 57; (p control) Df(2L)+/-, n = 32; (g) git, n = 21; (g, r1) git, rho1+/-, n = 20; (g, rg2) git, rhoGEF2+/-, n = 57; (g control) Df(2R)+/-, n = 23; (p,g) dpix, git, n = 37; (p, g, rg2) dpix, git, rhoGEF2+/-, n = 36; (p, g control) dpix+/-, git +/-, n = 19. Significance: * = p < 0.05; **** = p < 0.0001; ns = not significant. (C) Representative images of ovary development and egg production. Genotypes from left to right are: (control) Df(2L)+/-; dpix; dpix, rho1+/-; dpix, rhoGEF2+/-. (D) Reducing the gene dose of myosin activators increases mature egg length in git mutants and rescues egg length in dpix mutants. Upper and lower box edges represent upper and lower quartile boundaries, whiskers represent min to max. Genotypes and sample sizes are as follows: (wt) wild-type, n = 51; (g) git, n = 18; (g, rg2) git, rhoGEF2+/-, n = 73; (p) dpix, n = 108; (p, rg2) dpix, rhoGEF2+/-, n = 97. Significance: **** = p < 0.0001; ns = not significant. (E) Illustration of average aspect ratios for the indicated genotypes.