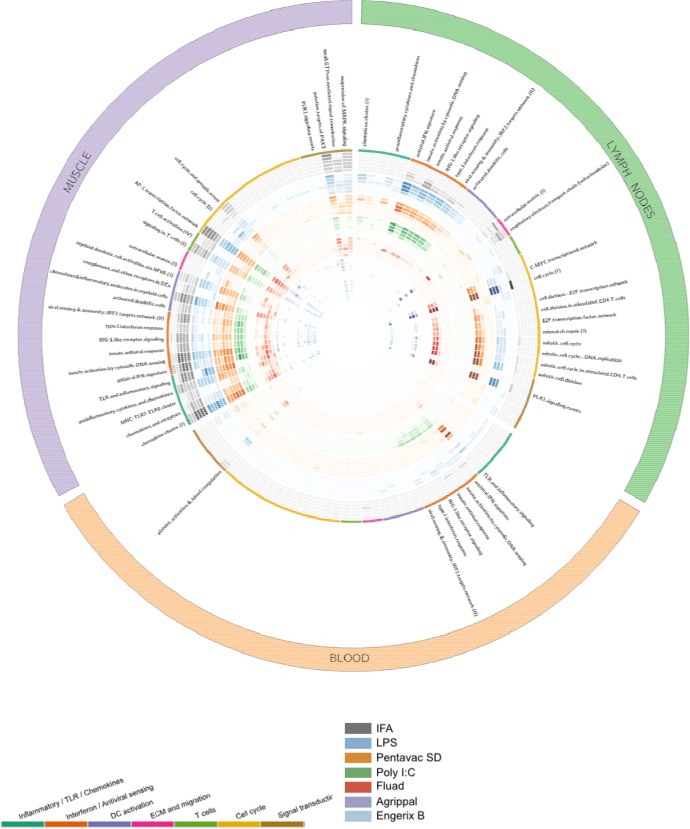
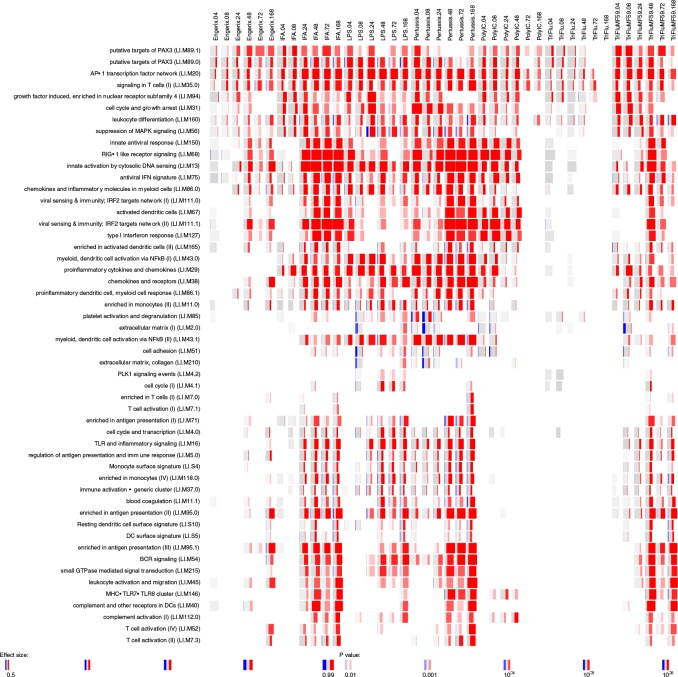
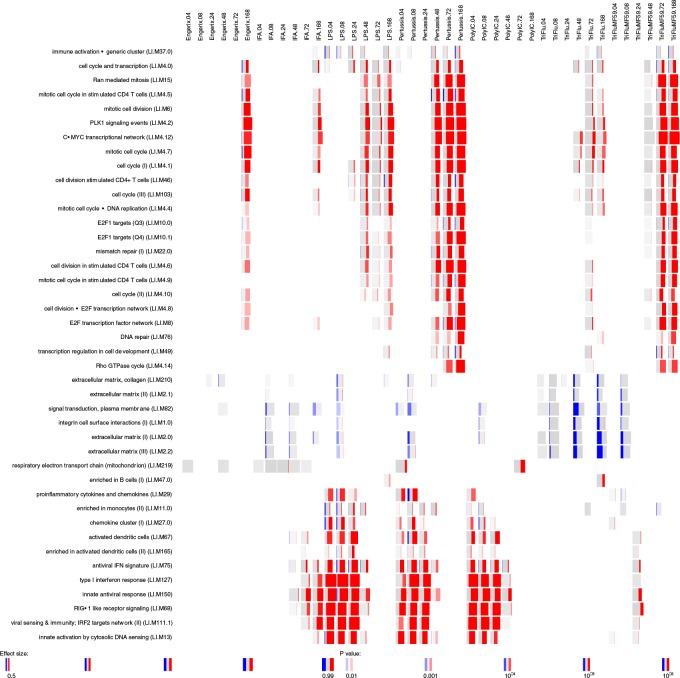
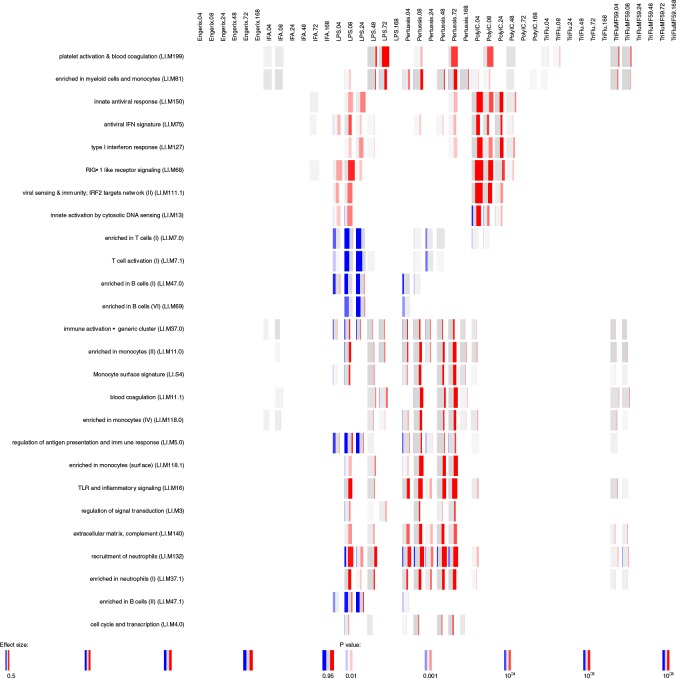
Figure 2. Gene-set enrichment analysis reveals distinct mechanisms of transcriptional response to the injected vaccines and TLR agonists.
Tissue data sets are presented as three coloured segments along the perimeter for the injected muscle (purple), the draining lymph nodes (green), and the blood compartment (red). An ordered list of blood transcriptional modules is labelled inside the outermost perimeter. Coloured bands adjacent to the module names correspond to the vaccines and Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists (outside to inside bands): incomplete Freunds adjuvant (IFA) (grey), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (blue), Pentavac SD (orange), Poly I:C (green), Fluad (red), Agrippal (purple), and Engerix (blue). For each band, there are six rings corresponding to time points 4, 8, 24, 48, 72, 168 hr (from outer to inner ring). The intensity of colours indicates the significance of the enrichment. Only modules with p-value for enrichment of <10−6 and an effect size (AUC) >0.8 are shown. DC, dendritic cell; ECM, extracellular matrix.