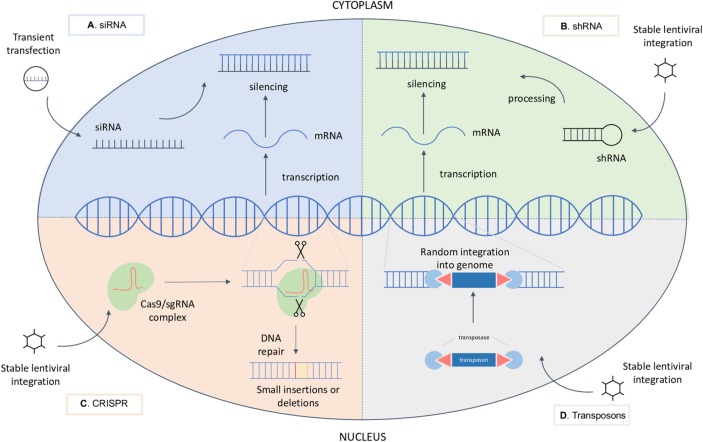
Figure 2.
Molecular mechanisms of genetic perturbations (A) siRNA molecule is transiently transfected into the cell, where it binds and thus silences the target mRNA molecule. (B) shRNA is introduced in the cell trough viral infection. Upon stable integration into the genomic DNA, it is processed into an siRNA that silences the target mRNA. (C) CRISPR system is generally introduced in the cell trough viral infection. Upon stable integration into the genomic DNA, both Cas9 and the sgRNA are expressed. The endonuclease Cas9 and a sgRNA form, therefore, a complex causing a double-strand DNA break at a target location. Mistakes during DNA repair can cause mutations at the break site. (D) Upon viral infection, transposon and transposase enzyme integrate into the genomic DNA and lead to random insertions in the genome, thus disrupting genes. CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeats;mRNA, messenger RNA; sgRNA, single guide RNA; siRNA, small interfering RNA; shRNA, short hairpin RNA.