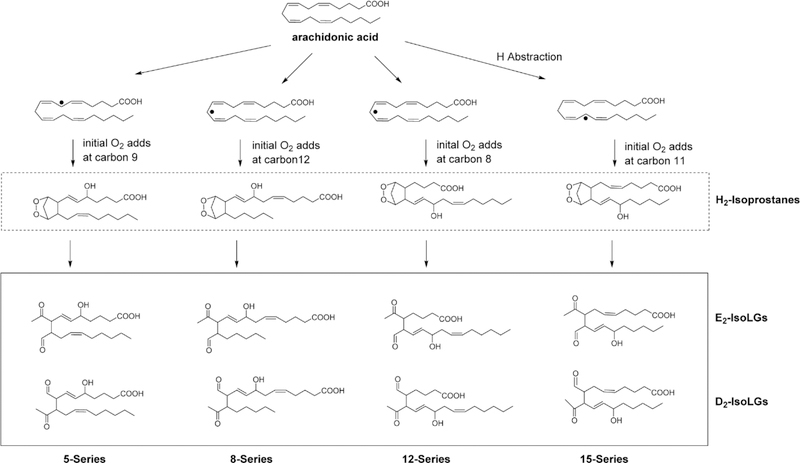
Figure 2. Formation of isolevuglandins (IsoLGs) from arachidonic acid via H2-isoprostane intermediates.
Radicals such as the hydroxyl or a lipid peroxyl radical can abstract a hydrogen from any one of three potential positions on a molecule of arachidonic acid to form a lipid radical. Because these carbon centered radicals form between two double bonds, the resulting electron is conjugated across the five adjacent carbons. Depending on at which position that molecular oxygen (a diradical) adds to these conjugated carbon centered radical, any one of four different regioisomers of the bicyclic endoperoxides (H2-isoprostanes) can form. Each of these regioisomers can give rise to two 4-ketoaldehyde regioisomers (D2-and E2-IsoLGs), generating a family of eight IsoLG regioisomers (and 64 stereoisomers since each regioisomer has 3 chiral carbons). These 4-ketoaldehydes then spontaneously react with primary amines such as lysyl residues of proteins or phosphatidylethanolamines.