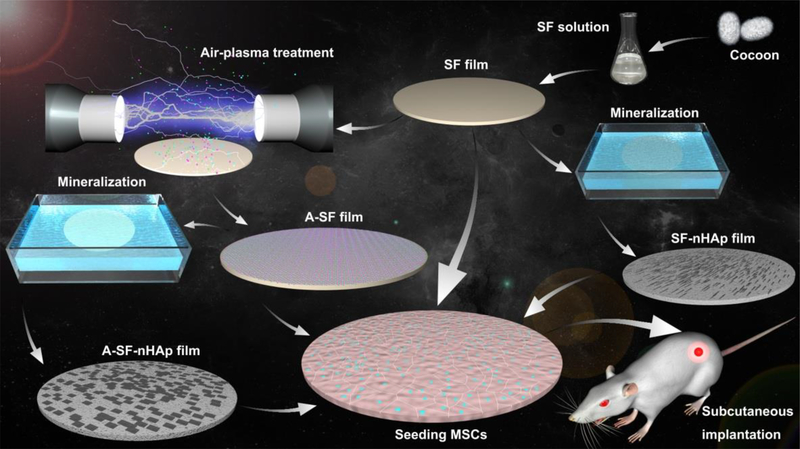
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration of the preparation, air-plasma treatment and mineralization of silk fibroin (SF) films as well as their use in inducing bone formation in vivo in a rat subcutaneous model. SF solution extracted from cocoon was fabricated into SF films by casting and soaking into a 70% (v/v) methanol solution. The SF films were treated with air-plasma for 5 min to become A-SF films. Both SF and A-SF films were futher mineralized to form needle-like and plate-like nano-hydroxyapatite (nHAp) on them, producing composite films termed SF-nHAp and A-SF-nHAp, respectively. The four films, SF, A-SF, SF-nHAp and A-SF-nHAp, were seeded with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and then subcutaneously implanted into the back of the rats. The A-SF-nHAP films promoted the ectopic bone formation most efficiently among all of the four groups.