Figure 1. Renal-clearable AuNPs enhanced renal elimination and retained cytotoxicity of DOX.
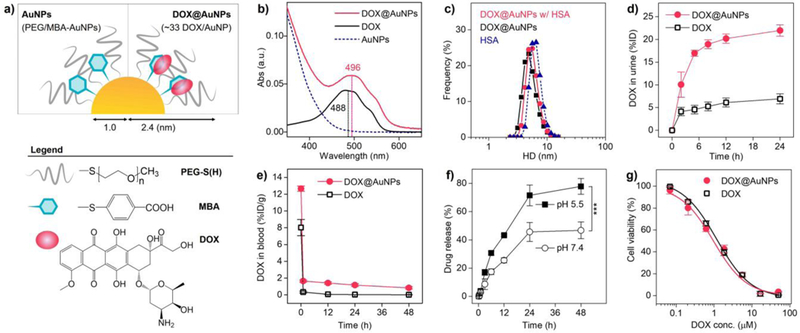
a) Scheme of renal-clearable DOX@AuNPs, which consists of the gold core (2.06 ± 0.18 nm in diameter, Fig. S2), surface coating with poly(ethylene glycol) thiol (PEG-SH, MW. 800 Da) and mercaptobenzoic acid (MBA), and loaded DOX molecules. b) UV-Vis absorbance spectra in aqueous solution. The loaded DOX exhibited 8-nm redshift (from 488 to 496 nm) compared with free DOX, indicating the formation of J-aggregates. c) Hydrodynamic diameters of DOX@AuNPs (5 μM) in PBS with and without human serum albumin (HSA, 6 nm, 5 μM) at 37 °C for 3 h. d) Renal clearance of DOX after intravenous injection of DOX@AuNPs and free DOX (n = 3). Error bar indicates s.d. e) Blood DOX concentration in the MCF-7 tumor-bearing mice (n = 4). f) In vitro drug release study in neutral (pH 7.4) and acidic (pH 5.5) physiological environment. ***P<0.005 (n = 3, Student’s t-test). g) In vitro cytotoxicity study with MCF-7 cancer cells (n = 6). To be noted, the AuNPs without DOX loading showed very low toxicity to the cells (Fig. S4d).
