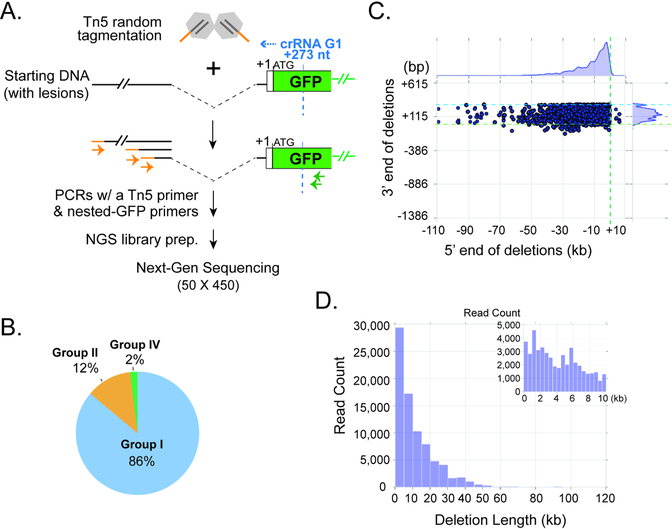
Figure 5. Tn5- and NGS- based characterization of Type I CRISPR-induced genome deletions.
(A) Schematic of Tn5 tagmentation procedure and NGS library construction. (B) Pie chart of three main types of lesion-containing reads identified by Miseq analysis. Light blue, Group I (one deletion junction); orange, Group II (a deletion with a large [>=9 bp] insertion, including partial inversion); green, Group IV (two deletions). The coloring scheme and categorization for deletion junctions are consistent with Fig. 4B. (C) Scatter plot for all Group I lesion-containing reads, showing the upstream (5’, X-axis) and downstream (3’, Y-axis) end points of the chromosomal deletions, relative to the EGFP translation start site (+1) at the DNMT3B locus. Dashed green line, and light blue lines, the (+1) start of the EGFP ORF; dashed blue line, recognition site for Cascade-G1. Kernel density estimates for the marginal distributions are shown along the axes, revealing the narrow range of downstream deletion endpoints and very long-tailed distribution of upstream deletion endpoints. (D) Histogram showing the distribution of deletion lengths observed for all the Group I reads in (B). The inset view on the top right corner is a zoom-in on deletions smaller than 10 kb.