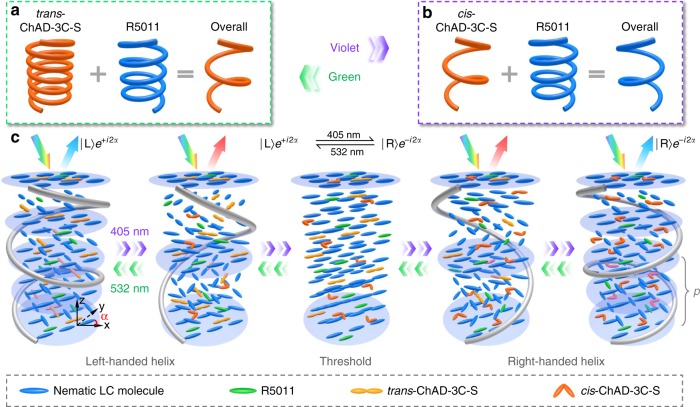
Fig. 1.
Chirality invertible CLC superstructure directed by light. a, b Mechanism illustration of the chirality inversion of ChAD-3C-S and R5011 mixture. c Schematic illustrations of CLC superstructure evolution driven by the violet (405 nm) and green (532 nm) light. The colorful arrows indicate a white incident light, while blue/red indicates shorter/longer wavelength of Bragg reflected light. z depicts the axis of the CLC helix, α is the initial orientation angle of local standing helix with respect to x-axis, L left circular polarization, R right circular polarization