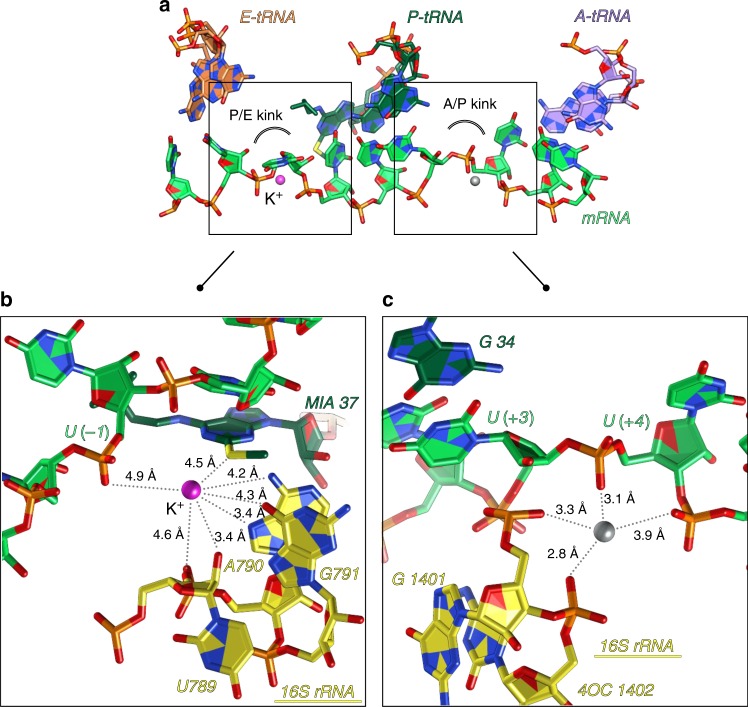
Fig. 3.
Metal ions in the mRNA path in elongation complex. a Along its path in the ribosome, mRNA gets distorted between A- and P- sites (A/P kink) and between P- and E-sites (P/E kink). Together with 16S rRNA nucleotides, these distortions represent negatively charged pockets, favorable for occupation by metal ions like K+ or Mg2+. b A K+ ion was identified in the P/E kink of the elongation complex. According to the distances, this K+ ion is most probably hydrated and may interact with 2-methylthio-N6-isopentenyladenosine (MIA) modification in the P-tRNAPhe and U(-1) in mRNA. c The cation identified in A/P kink was assigned as Mg2+ in the elongation complex, however, we include the possibility that it can be a different ion (probably an ammonium ion). Color code: colors are as in Fig. 2 with unidentified ion shown in gray