Figure 5.
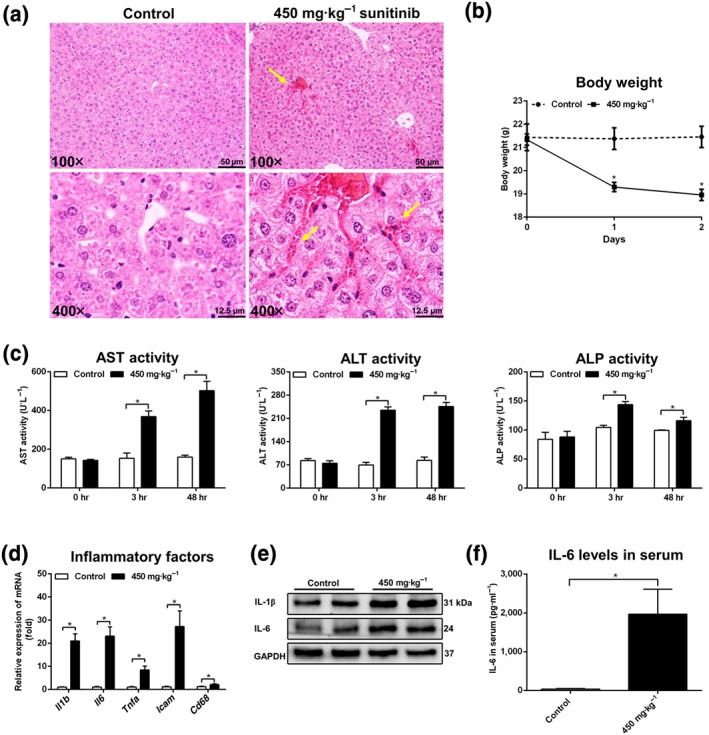
High‐dose sunitinib induced severe liver injury. (a) Haematoxylin and eosin staining of liver treated with 450 mg·kg−1 sunitinib. Haemocytes were shown by yellow arrowheads in 450 mg·kg−1 sunitinib groups. (b) Body weight was significantly decreased after 450 mg·kg−1 sunitinib treatment. (c) Aspartate transaminase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) enzyme activity was significantly increased in 3 and 48 hr serum. (d) Real‐time PCR analysis of inflammatory factors in liver. All inflammatory factors were significantly increased after 450 mg·kg−1 sunitinib treatment. Values represented fold change after normalization to control. (e) Western blotting was used to measure IL‐1β and IL‐6. IL‐1β and IL‐6 levels were significantly increased after 450 mg·kg−1 sunitinib treatment. (f) IL‐6 levels in 48 hr serum were significantly increased. All data were plotted as mean ± SEM (n = 5). *P < 0.05, significantly different as indicated
