Fig. 1.
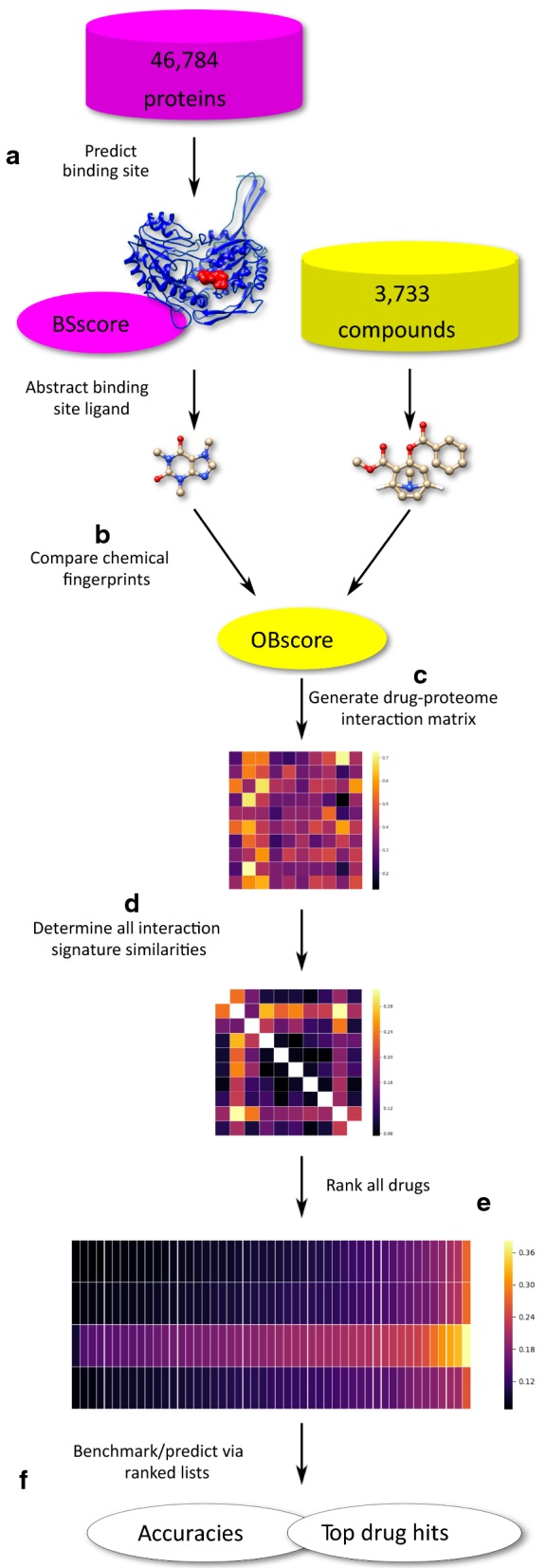
CANDO platform workflow. a Binding sites are predicted for each of the 46,784 proteins in the CANDO protein structure library using the bioinformatic tool COFACTOR [20–23], resulting in a BSscore. b The native ligand in the predicted binding site is compared to all 3,733 compounds in the CANDO putative drug library by calculating the chemical fingerprints using the FP4 fingerprinting method in Open Babel for each structure, resulting in an OBscore [24]. c Each compound-protein interaction is given a score based upon the OBscore and/or BSscore, which is then used to populate the interaction matrix. d The similarity score between every pair of compound-proteome interaction signatures (the vectors of 46,784 interaction scores) is calculated by root-mean-squared deviation (RMSD) which are then used to populate the compound-compound similarity matrix. e The compound-compound similarities are sorted and ranked by RMSD. f Benchmarking is accomplished by measuring the recovery rate of the known approved drugs, i.e., per indication accuracies are obtained based on whether or not pairs of drugs associated with the same indication can be captured within a certain cutoff of each of their ranked compound similarity lists; other similar compounds that fall within a particular cutoff are hypothesized to be repurposeable drugs and serve as predictions. The CANDO platform utilizes a proteomic approach for drug repurposing, with the hypothesis that drugs with similar interaction signatures will behave similarly
