Figure 1.
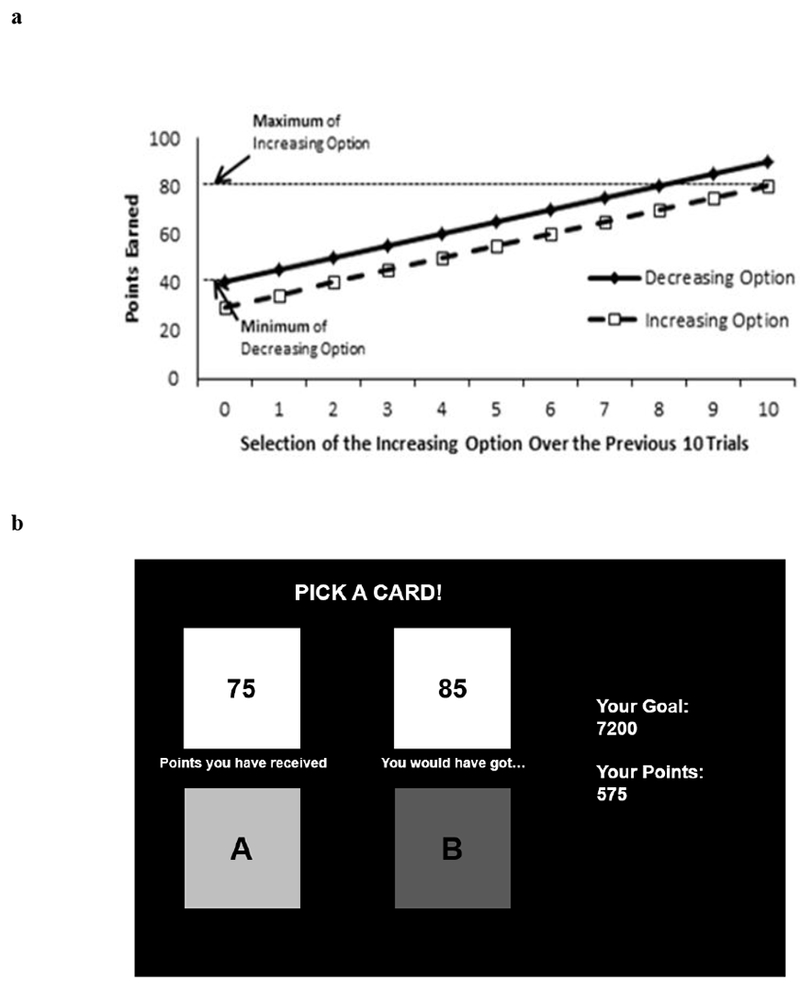
(a) Decision-making task reward structure. Rewards were a function of the number of times participants selected the Increasing option over the previous ten trials. If participants selected the Increasing option on all ten of the previous trials, then they would be at the right-most point on the x-axis. If they selected the Decreasing option on all ten of the previous ten trials then they would be at the left-most point on the x-axis. There is a consistent 10-point difference in rewards given for the Increasing (dotted line) and Decreasing (solid line) options. (b) Sample screenshot of the dynamic decision-making task with foregone reward feedback in which participants were shown what they “would have got” had they selected the other option.
