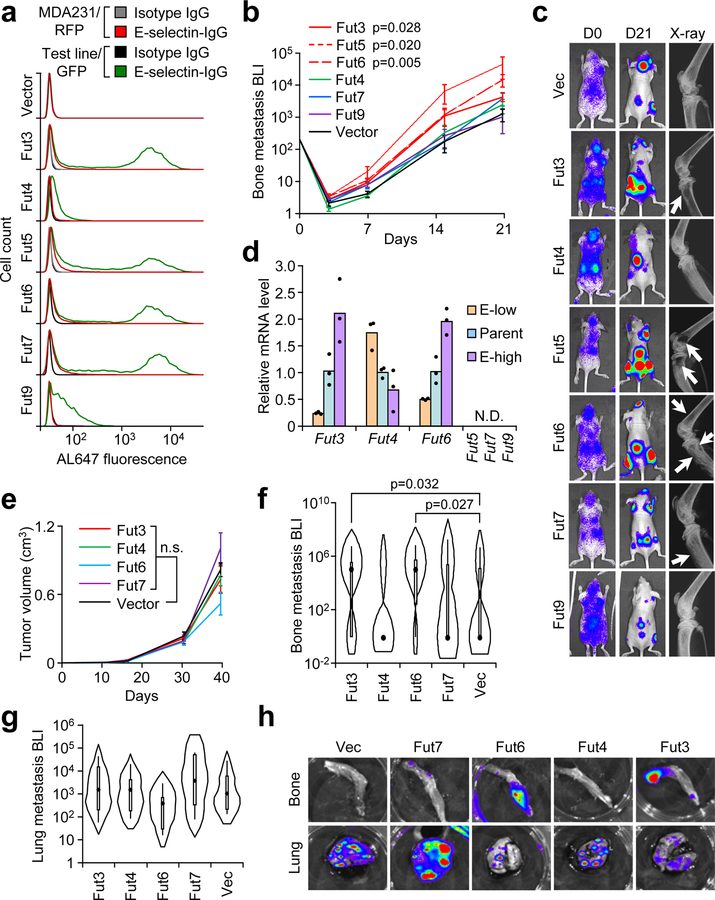
Figure 2. Specific α1–3 Fucosyltransferases (Fut3 and Fut6) promote bone metastasis.
(a) Comparative flow cytometry analysis of E-selectin binding to MDA-MB-231 cells with stable ectopic expression of α1–3 Fut enzymes. MDA-MB-231-RFP was used as an internal control. Data representative of four independent experiments. (b) BLI quantification of bone metastasis burden following intracardiac injection of M1a cells stably expressing each Fut enzyme into Nu/Nu mice. n = 6 (Fut3, Fut4, Fut6), 5 (Fut5, Fut9), 3 (Fut7), and 10 (Vector) mice. Statistics by Mann-Whitney U test at Day 21, two-sided. (c) Representative BLI and X-ray images of bone lesions from (b). White arrows indicate osteolytic lesions. (d) qPCR analysis of endogenous α1–3 Fut mRNA levels in the parental and sorted MDA-MB-231 cells with differential E-selectin binding abilities. Fut5/7/9 were not detectable (N.D.) in all cell lines. n = 3 technical replicates. (e) Tumor volume measurements after orthotopic injection of M1a cells stably-expressing each relevant Fut enzyme into NSG mice. p > 0.05 for all between-group comparisons by two-sided Student’s t-test at Day 39. n = 6 mice/group. (f,g) Violin plot showing BLI quantification of spontaneous bone (f) and lung (g) metastasis burden. Plot elements include median, box for interquartile range, spikes to upper- and lower- adjacent values. Statistics by Mann Whitney U test, one-sided. n = 11 lung/22 hindlimb (Fut3 and Fut 4), 6 lung/12 hindlimb (Fut 6 and Fut 7), and 12 lung/24 hindlimb (Vector). (h) Representative BLI images of bone and lung tissues from each experimental group. Experiment performed once (e-h). Data represent mean ± SEM. No statistically significant difference (p>0.05) between Fut4, Fut7, and Fut9 groups vs Vector group in b, Fut 4 and Fut 7 groups vs Vector group in f, and any group vs Vector group in e and g.