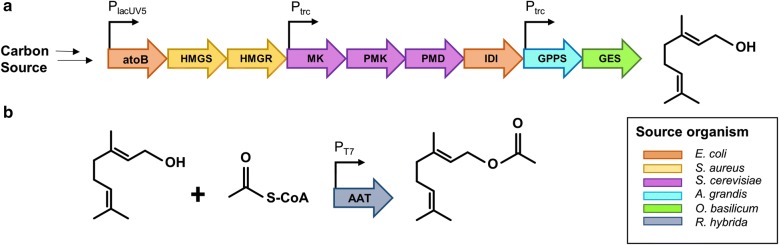
Fig. 1.
Diagram of the two E. coli expression constructs used in this study harbouring a the heterologous mevalonate pathway (MEV) leading towards the production of geraniol as expressed by pGER, and b an alcohol acyltransferase (AAT) capable of esterifying geraniol and acetyl-CoA to produce geranyl acetate as expressed by pET28a::RhAAT. Co-transformation of E. coli with the two plasmids, results in the production of geraniol and in vivo conversion to a geranyl acetate ester in high titres. The origin of all enzymes expressed on each plasmid is colour coded according to species of origin (inset)