Figure 1. Wood smoke particle exposure induces neutrophilic airway inflammation in healthy volunteers.
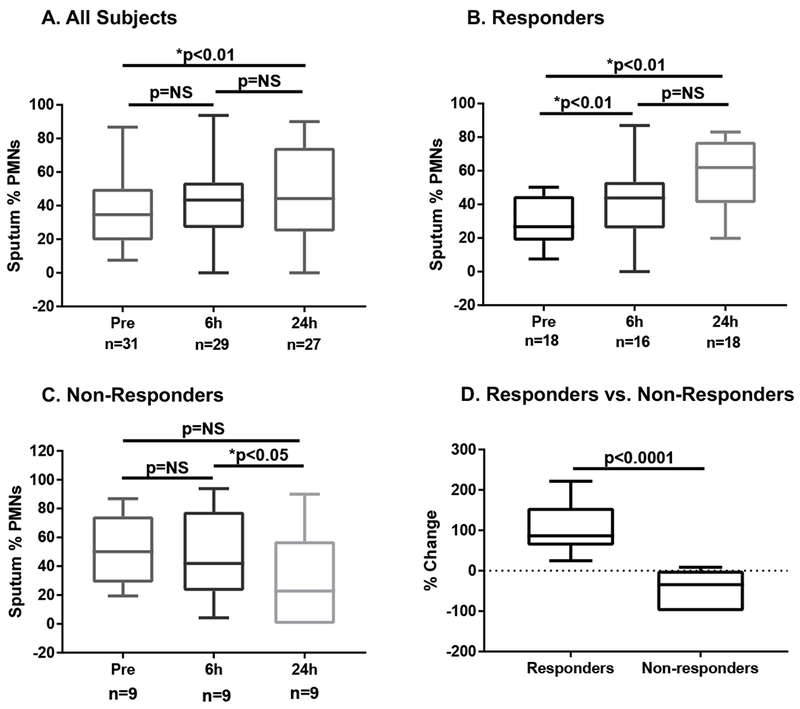
Healthy volunteers underwent exposure to WSP and provided induced sputum samples before exposure and 6 and 24 hours after exposure. A) All participants; B) Responders, defined by a ≥ 10 percent increase in sputum %PMNs; C) Non-Responders; D) Responders experienced a significantly greater change in sputum %PMNs from baseline at 24 hours post-WSP exposure compared to non-responders and all participants. Wilcoxon-signed rank tests were used to compare post-WSP sputum to baseline sputum (data represented as mean ± SEM; p values derived from log transformed data).
