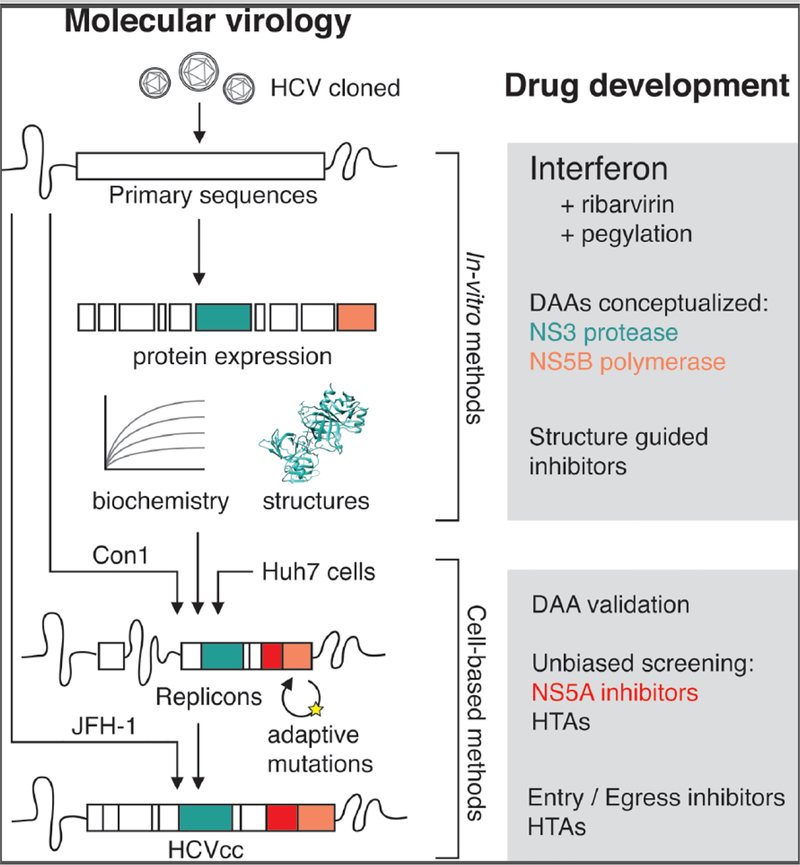
Figure 1: Domesticating hepatitis C virus.
After a decade and a half of observation as NANBH in humans, the cloning of HCV initially permitted in vitro expression, biochemical characterization, and structural studies of viral proteins. These studies subsequently informed the successful creation of the HCV replicon, a major breakthrough for validation, optimization and unbiased screening of DAAs and host-targeting agents (HTAs). This continued with HCVcc, which allowed drug development efforts encompassing the entire virus lifecycle. Major themes in drug development based on biochemical or cell-based models are presented in boxes at right.