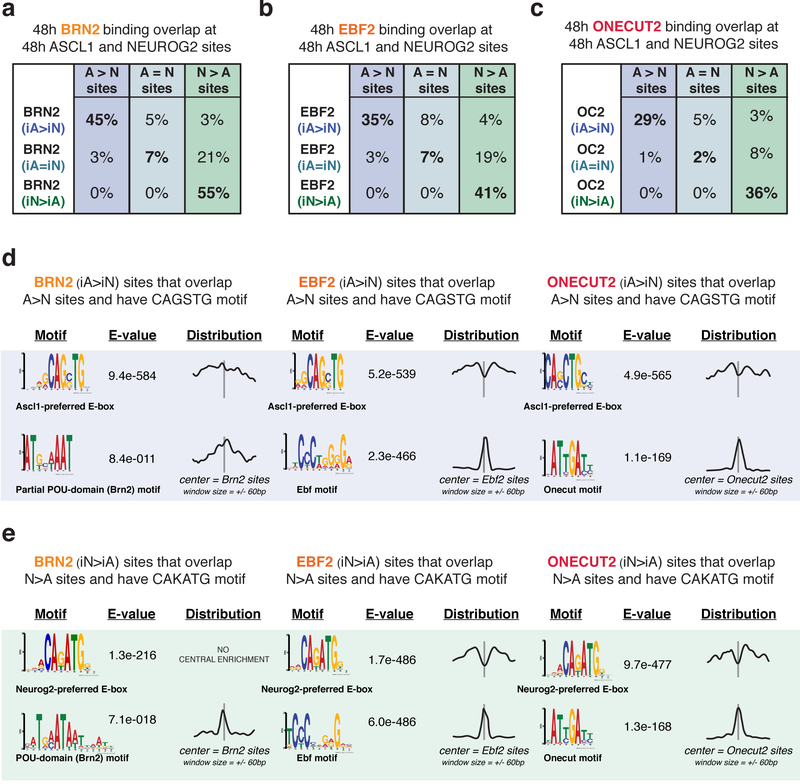
Fig. 6: Differentially bound sites of downstream TFs in iA or iN neurons overlap with Ascl1 or Neurog2 binding.
a-c, A subset of differentially enriched Brn2 (a), Ebf2 (b), Onecut2 (c) binding sites in iA or iN neurons at 48h overlap with Ascl1 or Neurog2 differential binding at 48h. d, MEME motif search at the 48h differentially bound Brn2, Ebf2, and Onecut2 sites in iASCL1 neurons (iA>iN) that overlap with differentially bound Ascl1 sites (A>N) with CAGSTG motif. Note that the cognate motif of downstream TFs is present and Ascl1-preferred E-boxes are depleted in the motif distribution graphs centered on downstream TF motifs. The E-values are reported by MEME, and represent an estimate of the expected number of motifs with the same log likelihood ratio that one would find in a similarly sized set of random sequences. e. MEME motif search at the 48h differentially bound Brn2, Ebf2, and Onecut2 sites in iNEUROG2 neurons (iN>iA) that overlap with differentially bound Neurog2 sites (N>A) with CAKATG motif.