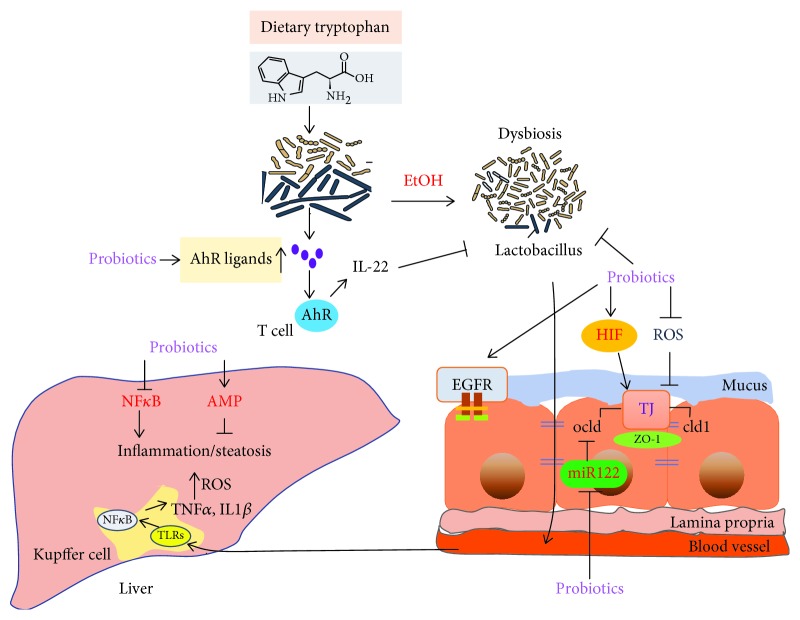
Figure 2.
Probiotics function in gut-liver mechanisms. Probiotics and related products prevent ethanol-induced effects in the intestine and the liver via multiple mechanisms: (1) enhancement of antioxidant activity; (2) reduction of inflammatory cytokine expression; (3) hepatic AMPK and induction of lipid metabolism; (4) enhancement of intestinal tight junction ZO-1, claudin-1, and occludin expression via increased intestinal HIF signaling; (5) inhibition of miR122a expression leading to occludin upregulation; (6) activation of EGFR and preservation of barrier function in intestinal epithelial cells; and (7) positive modification of gut microbiota and increase AhR ligands.