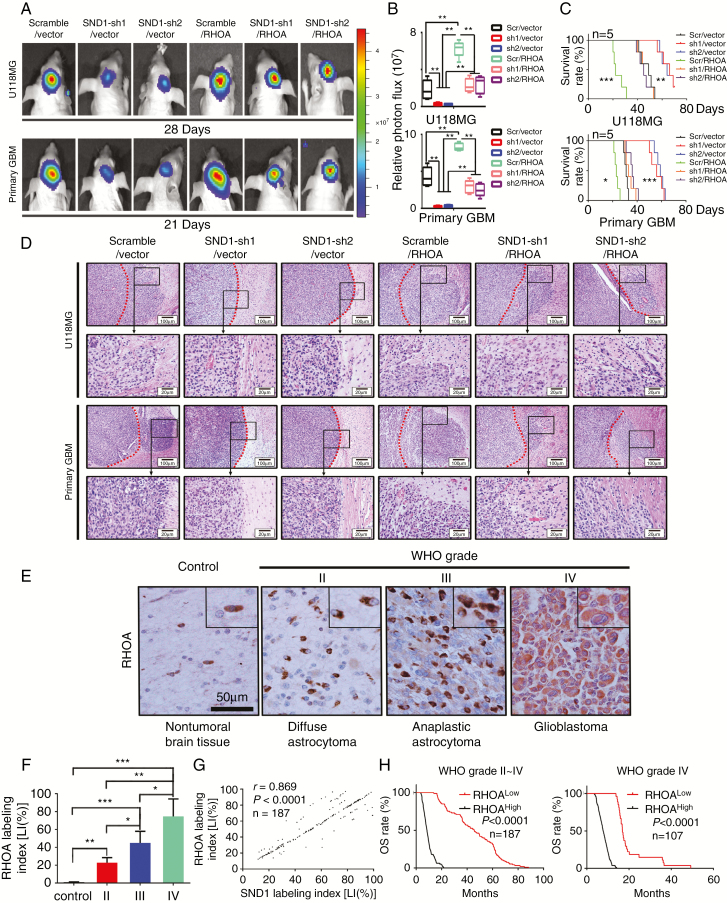
Fig. 6.
SND1 accelerates GBM in vivo growth via RhoA; the RhoA levels indicate high glioma grades and poor prognoses. (A) U118MG and primary GBM cells with empty vector plus scramble control shRNA (scramble/vector) or SND1 shRNA (SND1-sh1/vector, SND1-sh2/vector), or ectopic RhoA plus scrambled shRNA (scramble/RhoA) or SND1 shRNA (SND1-sh1/RhoA, SND1-sh2/RhoA) were inoculated orthotopically into NOD-SCID mice (n = 5). (B) Tumors were measured by the IVIS imaging system. (C) Survival analysis results of the tumor transplant experiment. (D) Representative HE-stained images of the invasion condition among the cells described in (A). Scale bar, 100 μm. (E) IHC results of RhoA expression. Scale bar, 50 μm. (F) Comparing the RhoA LIs among different WHO grades in 187 gliomas and 20 normal brain tissue samples. (G) Linear regression results showed the correlation between SND1 and RhoA in 187 gliomas. (H) Survival analysis results by RhoA LI in WHO grades II–IV glioma samples (left) and grade IV GBM samples (right).