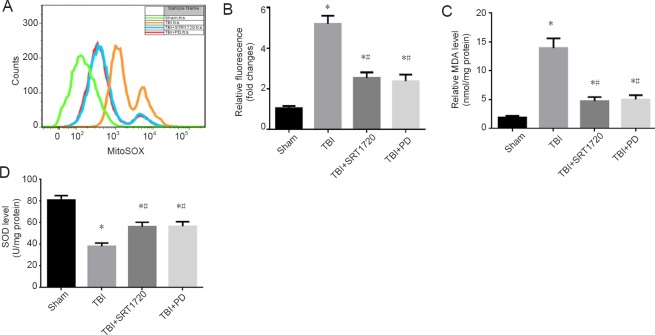
Figure 2.
Polydatin suppresses mitochondrial reactive oxygen species accumulation and oxidative stress response post-TBI.
(A) Neurons were isolated from the rat injured-side cortex, and were labeled with 4 µM MitoSOX for detection of mitochondrial superoxide. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (O2 –.) was detected using the fluorescent MitoSOX probe. Flow cytometry was used to analyze TBI-induced mitochondrial superoxide. (B) Quantification of mitochondrial superoxide post-TBI. (C) Quantification of MDA levels in the rat injured-side cortex detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. (D) Quantification of SOD levels in the rat injured-side cortex detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 6; one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparisons test). *P < 0.05, vs. sham group; #P < 0.05, vs. TBI group. PD: Polydatin; TBI: traumatic brain injury; MDA: malondialdehyde; SOD: superoxide dismutase; SRT1720: SIRT1 activator.