Figure 2.
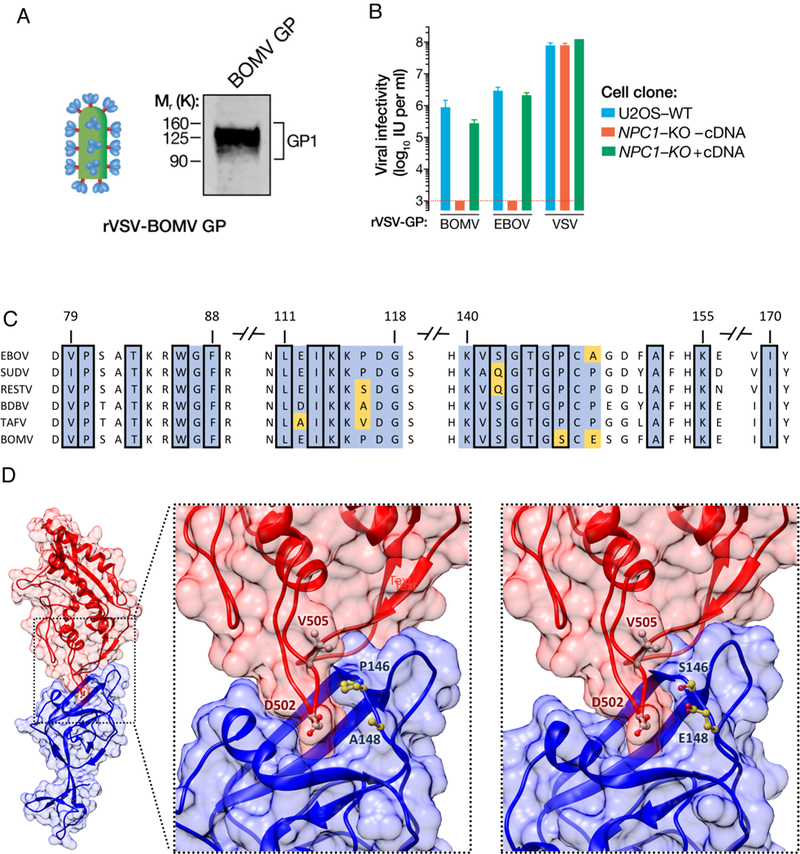
BOMV GP-mediated entry and infection is NPC1-dependent. (A) BOMV GP1,2 is incorporated in the rVSV particles detected by immunoblotting using ebolavirus anti-GP1 (B) Infectivity of rVSVs bearing BOMV, EBOV or VSV GP1 on WT or NPC1-KO U2OS cells complemented with or without human NPC1 cDNA. (C) GP1 alignment of the known human- infecting ebolaviruses (EBOV, SUDV, RESTV, BDBV, TAFV) and BOMV. Displayed regions pertain to the GP1 interface based on the GP1-human NPC1 crystal structure (PDB: 5F1B). Conserved residues in blue; viral-specific residues in yellow. Squared positions correspond to residues whose side chain heavy atoms are within 5 Â of any heavy atom in the human NPC1 receptor. (D) Left panel: Atomic representation of the interaction between the human NPC1 (red) and the EBOV GPi protein (blue) (PDB: 5F1B). Middle panel: Close-up view of the interface. Right panel: Close-up view of the modeled interface between the human NPC1 crystal structure (red) and the BOMV GP1 atomic model (blue). Displayed viral residues (in yellow) correspond to interfacial positions with different amino acids in the BOMV GP1 protein. Displayed residues on the human NPC1 (in white) correspond to residues with side chain heavy atoms within 5 Å of residues 146 and/or 148 in the EBOV or BOMV GP1.
