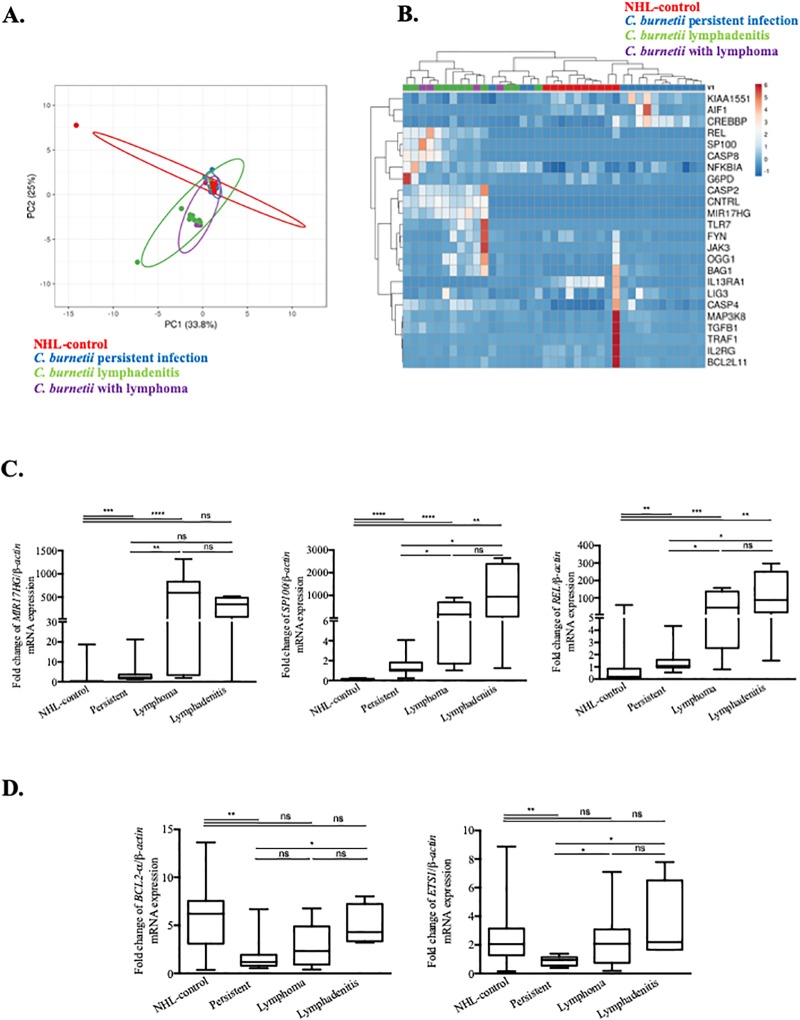
Fig 3. qRT-PCR analysis of disease-associated alterations in gene expression within the Cb-NHL signature.
PBMC samples from patients with acute Q fever, persistent C. burnetii infection, C. burnetii associated NHL, C. burnetii lymphadenitis and NHL-controls were compared to healthy controls by using qRT-PCR. The expression of genes from the Cb-NHL signature were evaluated as fold change of investigated gene/ β-actin mRNA. (A) Principal component analysis reveals the overlap between the modulated genes (log2 fold change) of the three groups of patients with persistent C. burnetii infection (blue), C. burnetii associated NHL (purple) or C. burnetii lymphadenitis (green) and NHL-control (red). (B) Modulated genes from Cb-NHL (log2 fold change) were represented as a heatmap with samples in columns and genes in rows. Gene expression was colored from blue (down-regulated) to red (up-regulated). (C) Comparison of patients affected by persistent C. burnetii infection to patients with lymphoma and lymphadenitis led to the identification of MIR17HG, REL and SP100 as significantly up-regulated in patients with lymphoma and lymphadenitis. (D) In patients with lymphadenitis, BCL2 and ETS1 were significantly up-regulated.