Figure 7. Type 2 diabetes is an aging-associated disease.
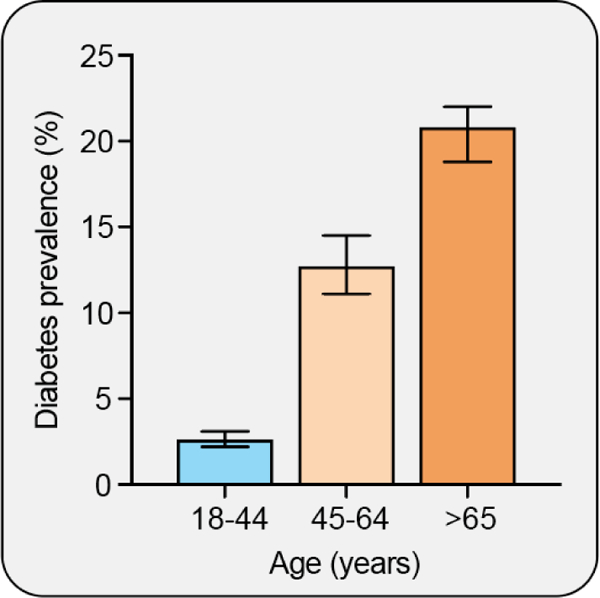
The prevalence of diabetes increases with age, and is substantially increased in the 65 and older population as compared to the 45 – 64 year old population (65).
Teaching points: The prevalence of diabetes increases with age and is nearly doubled in the 65 and older population as compared to the 45 – 64 year old population (65). Aging is also associated with insulin resistance that may be largely explained by a shift in adiposity from subcutaneous to visceral depots and an increase in ectopic fat accumulation.
