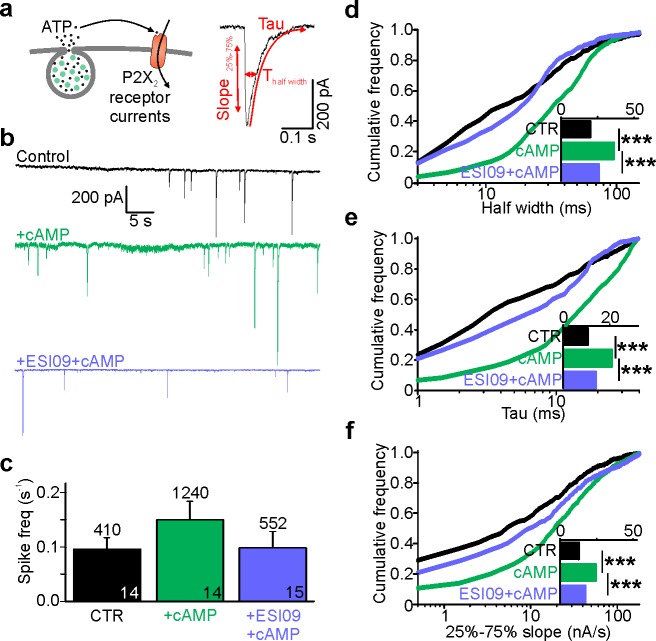
Figure 3. Cytosolic cAMP slows ATP release by activating Epac.
(a) Electrophysiological detection of nucleotide release events in INS-1 cells expressing P2X2-RFP. Cartoon of the assay (left) and example current spike (black) with fit and analysis parameters (red; Thalf, tau and slope during 25% to 75% of peak). (b) Representative P2X2 currents for control (black), and with cAMP (green) or with cAMP together with ESI-09 (purple) in the electrode solution. (c) Spike frequency conditions in (b). n of events (on top) and n of cells (on bars); two preps for each condition. (d–f) Cumulative frequency histograms of spike half width (d), decay constant tau (e), and slope of the rising phase (25% and 75% of peak, (f)) for CTR (n = 410 spikes, 14 cells), +cAMP (n = 1240, 14 cells) and +ESI-09 + cAMP (n = 552, 15 cells) with medians in the insets. cAMP increased half-width (p=4.1*10−31 vs ctrl, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test), tau (p=2.7*10−32, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test), and rising slope (p=4.7*10−19, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test); the effects were reversed by ESI-09 (p=3.4*10−21, p=3.6*10−22, and p=1.3*10−9, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test), respectively.