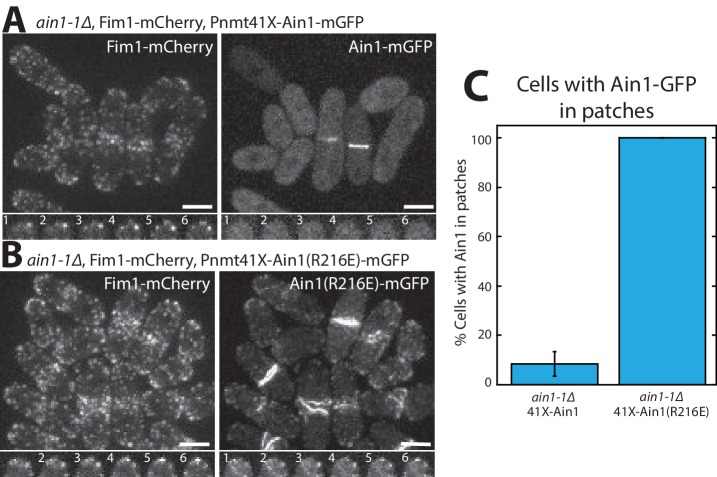
Figure 4. Fimbrin Fim1 and α-actinin Ain1 competition at actin patches is driven by their residence time on F-actin.
(A,B, top) Fluorescence micrographs of fission yeast in an ain1-1Δ background overexpressing GFP-tagged wild-type Ain1 (A) or mutant Ain1(R216E) (B) from the 41Xnmt1 promoter. Scale bars, 5 μm. (A,B, bottom) Timelapse (in s) of cell taken from a single Z-plane. (C) Percentage of cells in which Ain1-GFP is observed in actin patches. Error bar, s.e. Two-tailed t-test for data sets with unequal variance yielded p-value=0.0029.