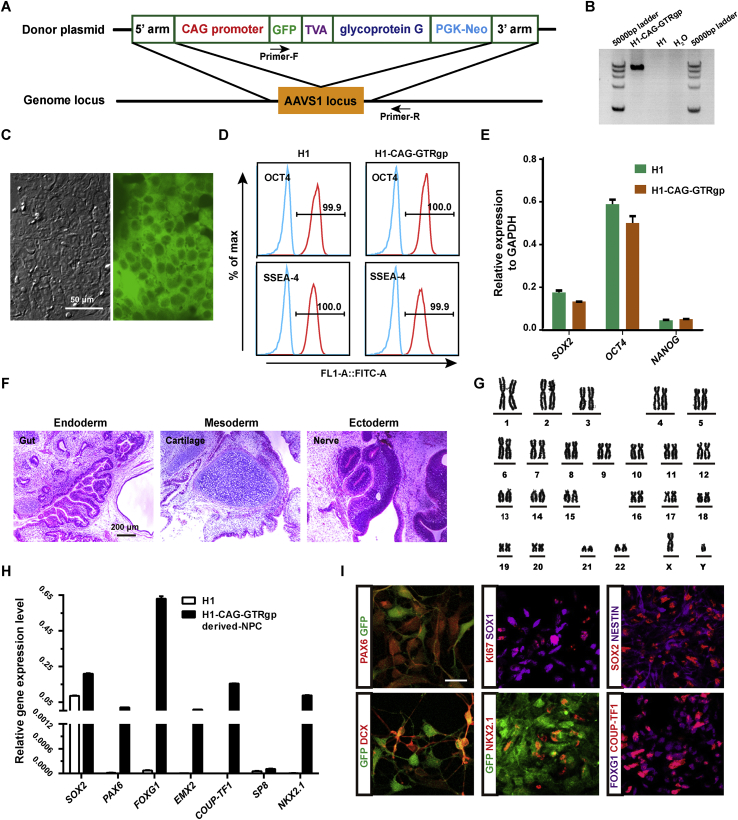
Fig. 1.
H1-CAG-GTRgp cells differentiated into neural progenitor cells with stable expression of GFP in vitro. A. Schematic diagram of the gene knock-in construct targeting the AAVS1 Locus. Donor plasmid containing homology arms to AAVS1 genomic regions (5′ and 3′ arms), CAG promoter, GFP, TVA, Rgp and PGK-neomycin cassette. B. Genotyping of the H1-CAG-GTRgp cell clones using the Primer-F and Primer-R primers, as depicted in (A). C. Representative GFP expression of the positive clones. Scale bar = 50 μm. D. OCT4 and SSEA4 expression levels in H1 and H1-CAG-GTRgp hES cells determined by FACS. E. SOX2, OCT4 and NANOG expression levels in H1 and H1-CAG-GTRgp hES cells determined by qRT-PCR. F. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the teratomas formed by H1-CAG-GTRgp hES cells. Scale bar = 50 μm. G. Karyotype of the H1-CAG-GTRgp hES cells. H. qRT-PCR analysis of different NPC markers in H1 hES cells and induced NPCs derived from H1-CAG-GTRgp hES cells. I. Representative immunofluorescent images of induced neuroepithelial cells, immature neuronal cells and neural progenitor cells derived from H1-CAG-GTRgp hES cells. Scale bar = 20 μm.