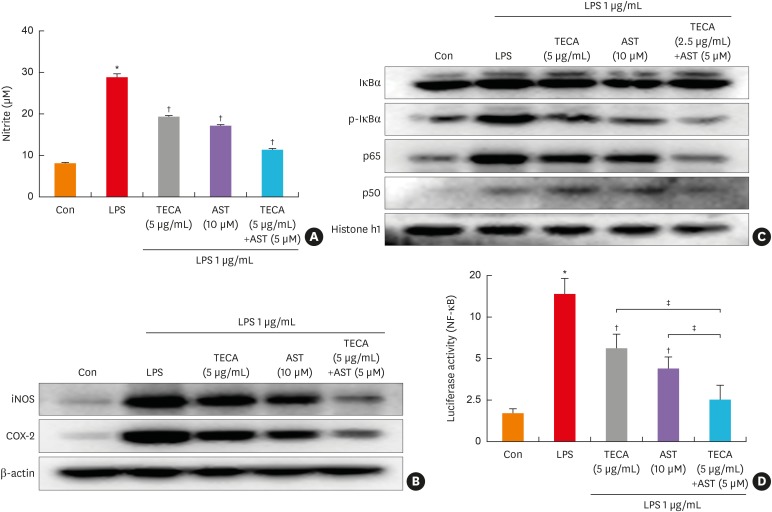
Fig. 5. Effects of the TECA + AST treatment on NO production and the expression of iNOS and COX-2 in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 macrophages. The cells were treated with 1 μg/mL LPS alone or LPS with TECA (5 μg/mL), AST (10 μM) and the combination of TECA (2.5 μg/mL) + AST (5 μM) for 24 hours. At the end of incubation, 50 μL of the medium was removed to measure NO production (A). Control values were obtained in the absence of LPS. In the culture medium, NO production was measured by the Griess reaction as described in Materials and Methods. Equal amounts of total proteins (20 μg/lane) were subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE, and alterations in the expression of iNOS and COX-2 proteins were detected by Western blotting using specific antibodies (B). The β-actin protein was used here as an internal control. The effect of the TECA + AST treatment on the LPS-induced translocation of the NF-κB subunits (p50 and p65) into the nucleus and the phosphorylation of IκBα in cytosol (C). Equal amounts of nuclear proteins (20 μg/lane) or total proteins (20 μg/lane) were subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE, and the expressions of p50, p65, IκBα and p-IκBα proteins were detected by Western blotting using specific antibodies. Histone h1 protein and β-actin protein were used here as internal controls. The effect of the TECA + AST treatment on the LPS-induced NF-κB transcriptional activity (D). Data shown are the mean ± standard deviation from 3 experiments in duplicate.
Con, control; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; TECA, titrated extract of Centella asiatica; AST, astaxanthin; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; COX, cyclooxygenase; SDS-PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
*P < 0.05 is the significance level compared to the control group. †P < 0.05 is the significance level compared to the PA treatment group. ‡P < 0.05 is the significance level compared to the TECA or AST treatment alone group.