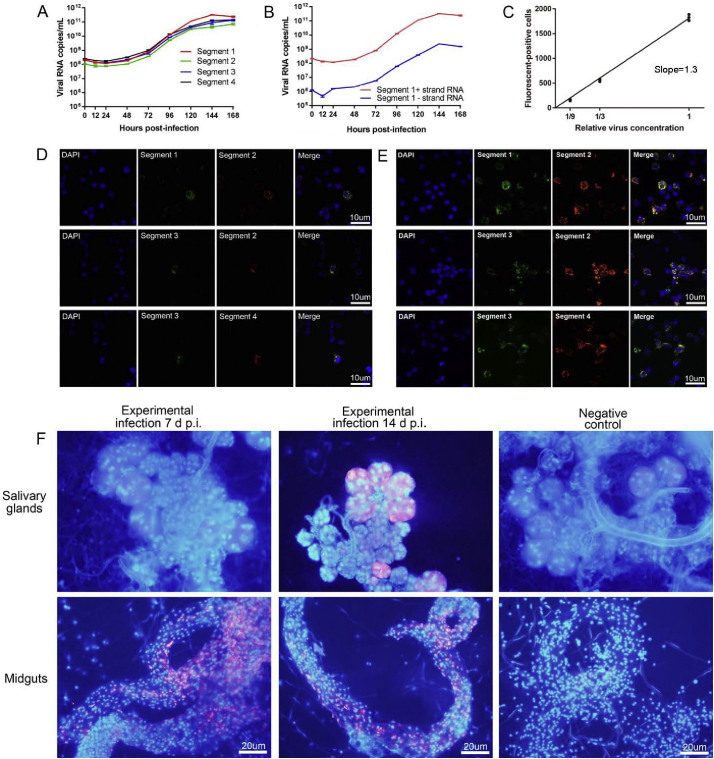
Fig. 1.
Biological features of JMTV in BME/CTVM23 cells.
Growth curves of each of the four genome segments of JMTV in BME/CTVM23 cells. The copy numbers of each viral segment were calculated by a standard curve method using a linearised plasmid containing the corresponding segment (Panel A). Detection of positive strand and negative strand of segment 1 by strand-specific quantitative PCR with a tagged primer system during growth in BME/CTVM23 cells (Panel B). The dose-response curve for JMTV. The count of fluorescent-positive cell for representative segment 2 probe sets per 104 cells is shown on the y axis, and the relative viral dilution is shown on the x axis (Panel C). Detection of each genome segment of JMTV in infected BME/CTVM23 cells by fluorescence in-situ hybridisation (FISH). Cells were fixed at 72 h (Panel D) and 144 h (Panel E) post infection respectively. Magnification×200. Detection segment 2 probe sets-JMTV FISH in salivary glands and midguts of male A. javanense experimentally-infected at 7 and 14 days post infection. Nuclei, DAPI (blue), Segment 2 probe, Quasar 570 (red). Magnification×400 (Panel F). Three biological replicates were run for experiments of Panel A to E. Five biological replicates were run for experiment of Panel F. Three technical replicates were run for all experiments. Estimates from the three technical replicates were averaged and error bars indicated standard error across biological replicates. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)