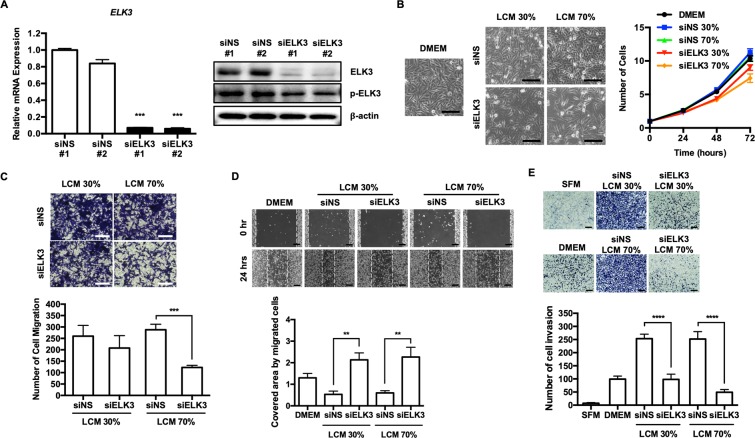
Figure 2.
The role of LCM in supporting the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro was associated with the expression level of ELK3 in LECs. (A) The suppression of ELK3 in LECs via the transfection of a siRNA targeting ELK3 was confirmed by qRT-PCR and immunoblot analysis. (B) MDA-MB-231 cell proliferation was assessed in DMEM, 30% siNS LCM, 30% siELK3, 70% siNS and 70% siELK3. MDA-MB-231 cell proliferation in 30% or 70% siELK3 LCM was significantly lower than that in DMEM, whereas the cell proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells in 30% or 70% siNS LCM was slightly higher than that observed in DMEM. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (C) The effect of siNS or siELK3 LCM on the migration of MDA-MB-231 cells was analyzed by a transwell assay. MDA-MB-231 cells educated in the indicated LCM were cultured in a transwell chamber for 24 h. The migrated cells were stained with crystal violet (Left) and quantified (Right). Scale bar represents 100 μm. (D) A scratch wound healing assay was performed to examine the effect of siNS or siELK3 LCM on the migration of MDA-MB-231 cells (Left). The cells were cultured in the indicated LCM, and migration was observed 24 h after scratching (Left) and photographed (Right). Scale bar represents 200 μm. (E) Matrigel invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells toward EGF in the presence of the indicated LCM. Scale bar represents 200 μm. Error bars represent the standard error from three independent experiments, and each experiment was performed using triplicate samples. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001 (Student’s t-test).