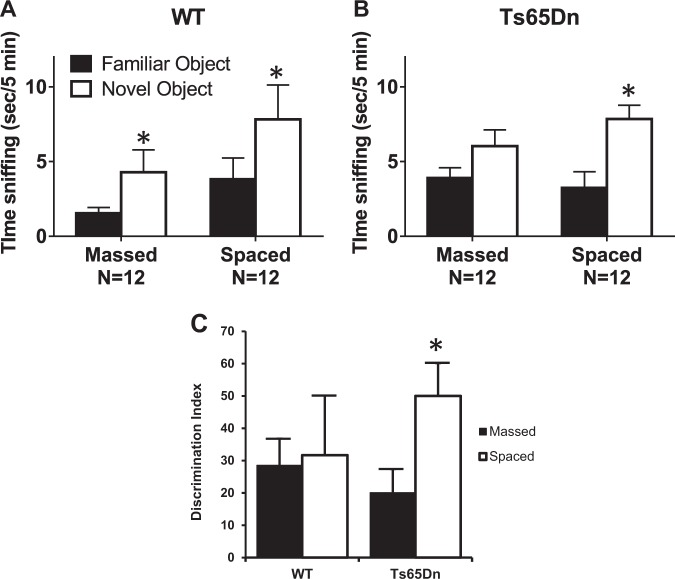
Fig. 2. Novel object recognition in WT and Ts65Dn mice.
Novel object recognition memory was detected in WT for both the massed and spaced training conditions. Ts65Dn did not display novel object recognition in the massed training condition, whereas the spaced training condition yielded significant novel object recognition. a WT displayed significantly more time exploring the novel object than the familiar object, both when training trials were administered consecutively (massed: t1,11 = 2.29, *p < 0.05), and when the three training trials were administered at 1 h intervals (spaced: t1,10 = 2.31, *p < 0.05). b Ts65Dn did not display a significant difference between time spent exploring the novel object and time spent exploring the familiar object (massed: t1,11 = 2.035, NS). Ts65Dn displayed significantly more time exploring the novel object than the familiar object when training trials were administered at 1 h intervals (spaced: t1,11 = 3.60, *p < 0.01). c Spaced training trials significantly elevated the DI in Ts65Dn, as compared to the DI in Ts65Dn given massed training trials (*p < 0.05). Interaction between genotype and training condition was not significant