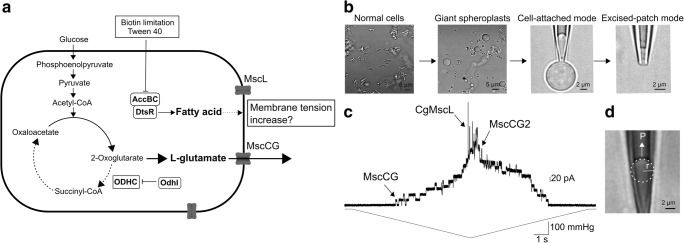
Fig. 1.
C. glutamicum glutamate production by mechanosensitive channels. a Mechanosensitive channel model for glutamate efflux. Biotin limitation and supplementation of tween 40 inhibit fatty acid synthesis and reduce the total amount of membrane lipids. Increased membrane tension activates exclusively the mechanosensitive channel MscCG and the glutamate is excreted by passive diffusion through the open pore of MscCG. bC. glutamicum giant spheroplasts preparation and application of patch clamp technique. c Current recording of all C. glutamicum endogenous mechanosensitive channels by mechanical stimuli in direct patch clamp. Upper and lower traces show channel currents and pressure applied to the membrane, respectively. d Measurement of membrane tension by Laplace’s law. P is pressure applied to the patch membrane, and r is radius of membrane curvature