Fig. 2.
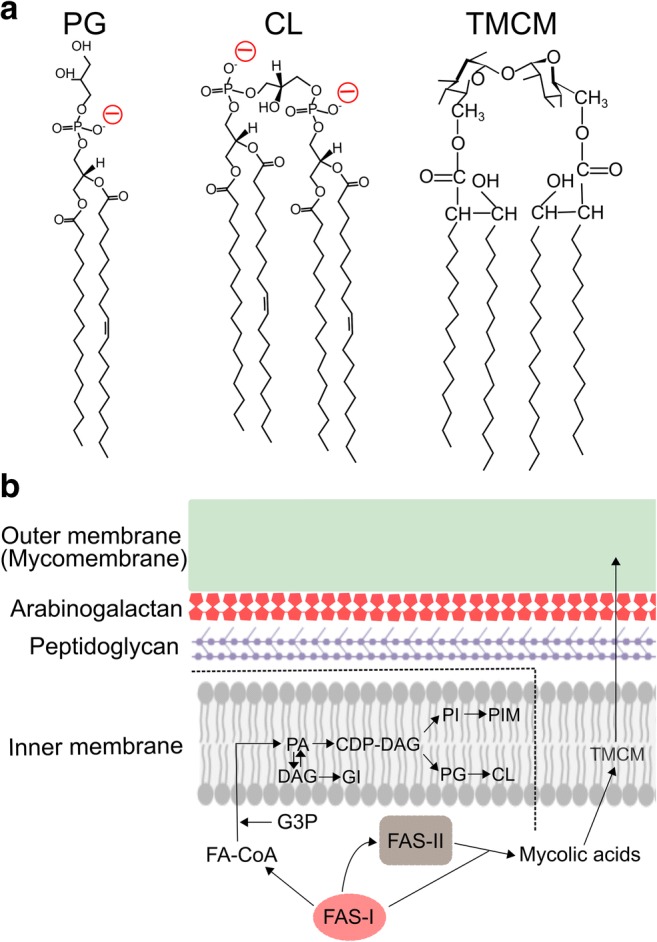
C. glutamicum membrane lipids and the cell envelope structure. a Structural membrane lipids of inner and outer membranes, phosphatidylglycerol (PG), cardiolipin (CL), and trehalose corynomycolate (TCMC). The negatively charged head groups of PG and CL are shown in red. b The structure of the C. glutamicum cell envelope and membrane lipid synthesis. As a branch point, phosphatidyl acid (PA) is biosynthesised by transferring an acyl chain from fatty acyl-CoA (FA-CoA) to glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P), and then forms cytidine diphosphate-diacylglycerol (CDP-DAG), the precursor for the synthesis of PI, PIM, PG, and CL. Thus, all phospholipids are synthesised in the inner membrane. PA is also dephosphorylated to become DAG and GI is synthesised from DAG. Mycolic acids are synthesised by FAS-I and FAS-II separately from phospholipids
