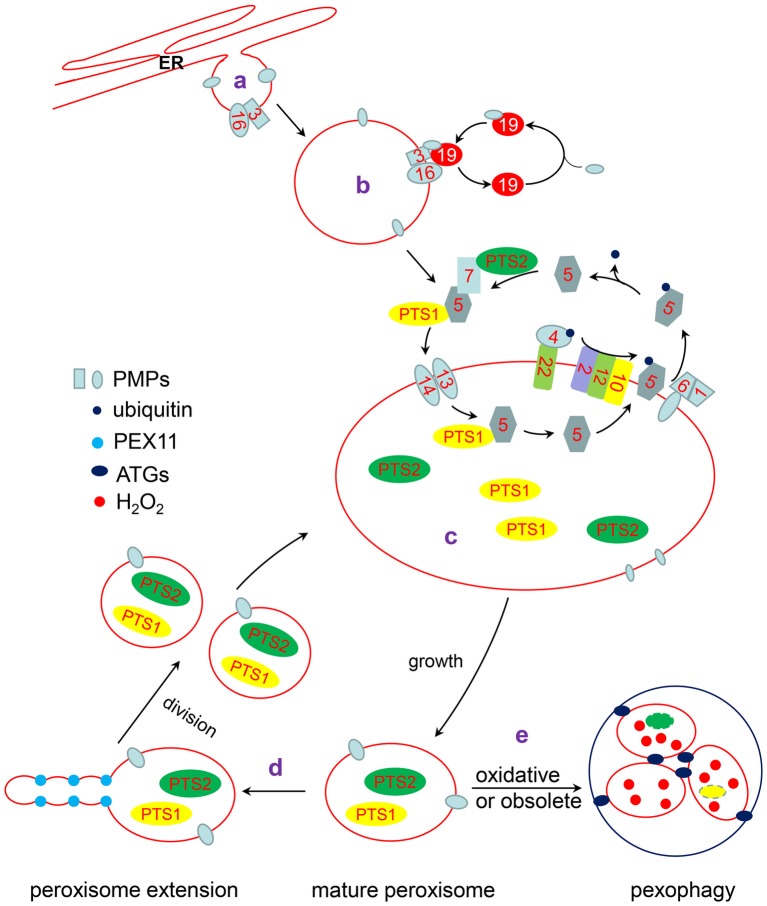
Figure 1.
The life cycle of peroxisome. a: Some PMPs are targeted to the ER and localized in special ER subdomains, where new preperoxisomes subsequently bud off. b: The remainder of PMPs are directly inserted into the peroxisomal membrane through a PEX3/PEX19-dependent pathway or another unknown pathway. c: PTS1 and PTS2 proteins interact with their receptor, PEX5 or PEX7, respectively. The receptor/cargo complex is then transported into the peroxisome lumen through the docking complex, composed of PEX13 and PEX14 in Arabidopsis. After unloading its cargo protein, PEX5 is mono-ubiquitinated by the PEX4/PEX22 (E2 ubiquitin conjugases) and PEX2/PEX12/PEX10 (E3 ligases) complexes. Subsequently, Pex5 is retrotranslocated to the cytosol by the PEX1/PEX6 complex for recycling. d: Mature peroxisomes elongate and divide into two new peroxisomes. e: Oxidative or obsoleted peroxisomes can be degraded by pexophagy under the action of ATGs.