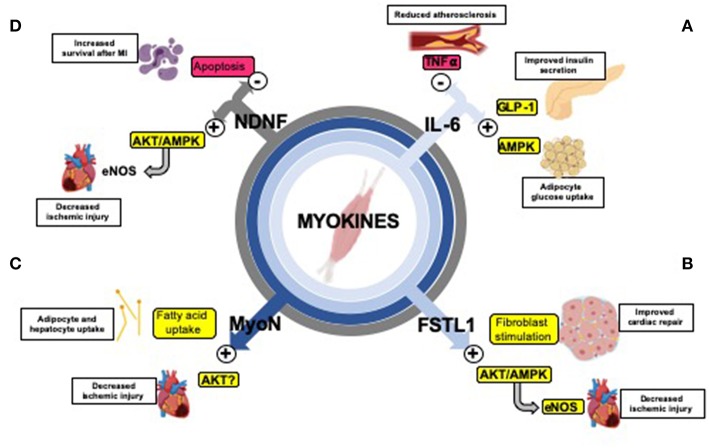
Figure 2.
Exercise-induced myokines mediate organ cross-talk and improve cardiometabolic health. (A) The myokine IL-6 inhibits TNF-α (186), reducing inflammation and protecting against the formation of atherosclerosis (187); stimulates GLP-1 secretion causing improved insulin secretion (188); increases lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation in adipose tissue (189) and increases glucose uptake through the AMPK signaling pathway (190, 191). (B) Fstl1 decreases ischemic injury size through activation of the Akt/AMPK pathway (activating eNOS and enhancing revascularization) (118, 119) and early fibroblast stimulation (which aids in repair after ischemia-reperfusion) (192). (C) Myonectin (MyoN) increases fatty acid uptake in adipocytes and hepatocytes (117), and promotes protects against ischemic injury in the heart, possibly through Akt activation (193). (D) NDNF improves survival after myocardial infarction (MI) by reducing apoptosis (120) through stimulation of the Akt/AMPK/eNOS pathway (enhancing revascularization) (194).