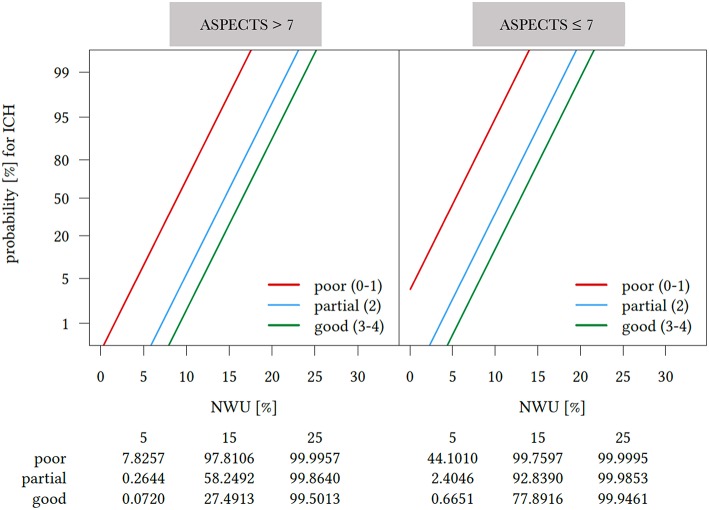
Figure 1.
Probability of intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) after successful endovascular treatment by collateral score, early Net Water Uptake (NWU) and ASPECTS after logistic regression analysis adjusted for age and sex. Impact of Net Water Uptake (NWU) (x-axis) and Alberta stroke program early CT score (ASPECTS), dichotomized for ASPECTS ≤7 and ASPECTS >7, and collateral score (straight lines) on the probability of intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) after successful recanalization (y-axis) based on multivarible linear regression analysis adjusted for sex and age. For any given early NWU, the probability for developing ICH was modulated by the level of collateral score and ASPECTS. The probability for ICH was higher for patients with poor collateral status, higher NWU. Colored lines indicate collateral scores [good (3–4); partial (2); and poor (3–4)]. Collateral Scores were grouped into good, partial, and poor collaterals (11). Dichotomization of ASPECTS was performed according to Cut-off Value in ROC-Analysis. ASPECTS, Alberta stroke program early CT score; ICH, Intracerebral hemorrhage; NWU, Net Water Uptake.