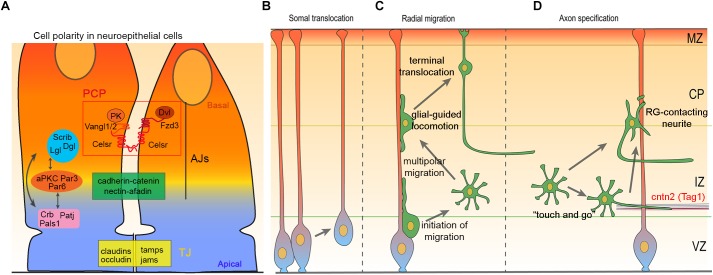
FIGURE 1.
Cell polarity, migration and axon specification in cortical development. (A) Schematic illustration of neuroepithelial apical junctional complexes: tight junction (TJ) and adherens junction (AJ) define apical–basal polarity and delineate cellular domains. These junctions regulate cell–cell adhesion, cellular transport and serve as an intracellular anchoring site for apical–basal polarity complexes, Crb-Pals1-PatJ, Par3-Par6-aPKC, and Scrib-Lgl-Dlg. Apical–basal polarity complexes interact with each other and with PCP proteins Celsr1-3, Fzd3/6, Vangl1/2, Dvl1-3, and Pk1-4, to establish and maintain cell polarity. (B–D) Diagram illustrating somal translocation (B), multi-phase radial migration (C), and axon specification in the cerebral cortex (D).