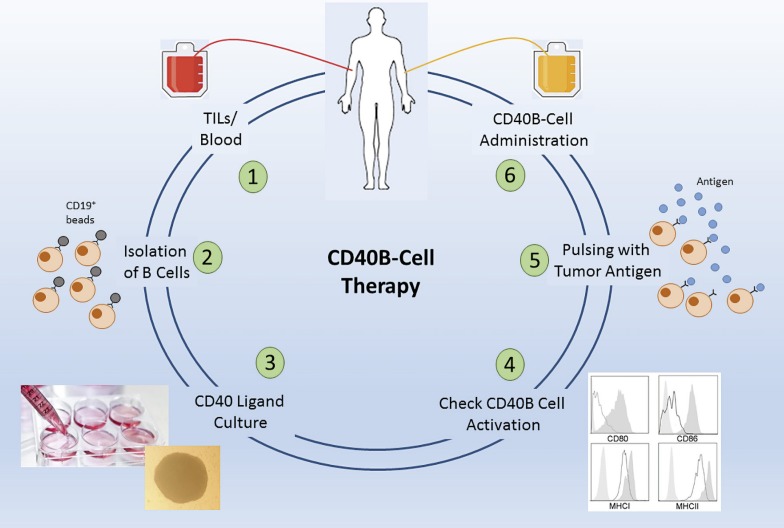
Fig. 1.
Concept of a possible CD40B-cell study. B cells can be isolated from tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte tumors (TIL) or alternatively from peripheral blood (1) by CD19 microbeads (2). After cultivation and expansion in the CD40L culture (3), the activation status is checked by determining the expression of the activation markers, CD80, CD86, MHC class I, and MHC class I, which are usually highly upregulated after CD40L stimulation (4). After pulsing with a suitable tumor antigen (5), CD40B cells are reinjected into the patient (6).