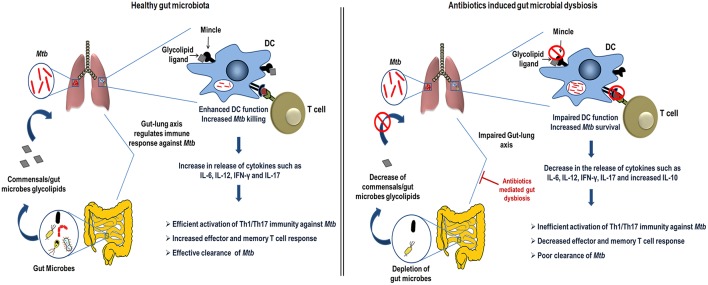
Figure 10.
Conceptual model of the study. During homeostasis, a healthy gut through microbial products such as glycolipids (synthetic analog, TDB that binds mincle) regulates lung immune response during Mtb infection. Gut commensals bacteria derived glycolipids reach lung via blood stream. In Mtb infected lungs, they bind to the mincle receptor expressed on DCs leading to their activated phenotype and functions such as production of immunoregulatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-12), which in turn elicits the CD4 T cells differentiation to Th1 and Th17 cells via the release of IFN-γ and IL-17 cytokines, respectively. Further, there is generation of memory response and protective immunity against Mtb in lungs. This immunoregulation through gut microbiota is disturbed upon the Abx induced dysbiosis. Abx depletes the beneficial commensals population, which is responsible for the impairment of DCs function and hence the dysregulated lung anti-Mtb immunity.