FIGURE 3.
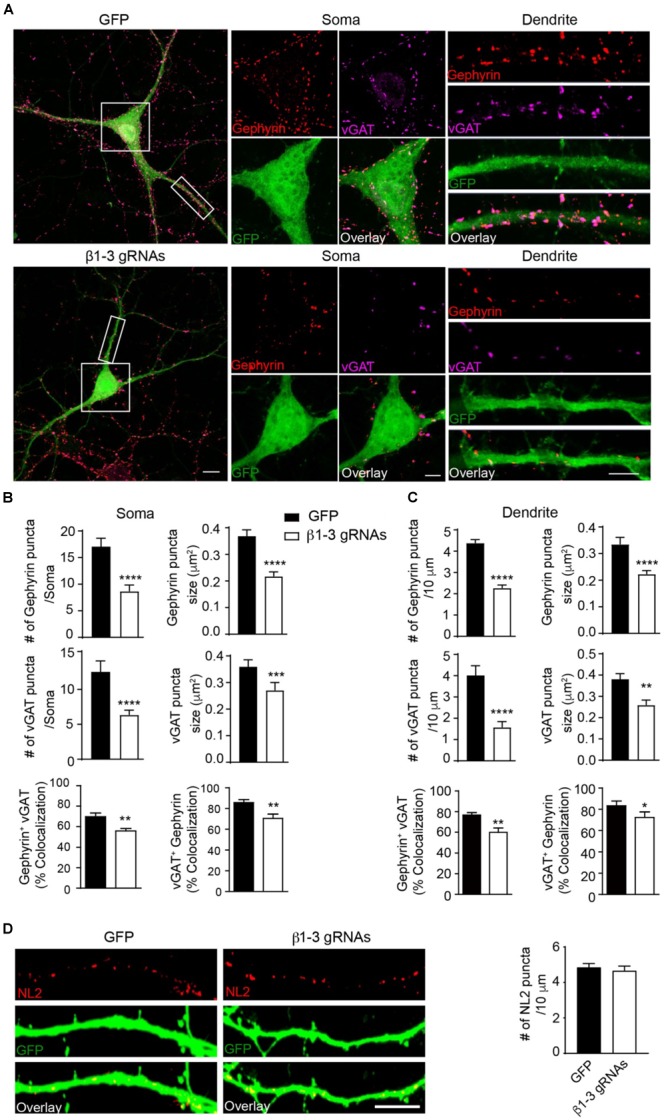
Loss of GABAARs strongly reduced inhibitory synapse density in hippocampal neurons. (A–C) Single-cell KO of GABAARs significantly reduced gephyrin (red) and vGAT (magenta) puncta as well as co-localization of gephyrin and vGAT in hippocampal neurons. (A) Representative images of gephyrin and vGAT-immunolabeling in neurons expressing GFP (top) or β1-3 gRNAs (bottom). (B) Bar graphs showed the quantitation of gephyrin (top), vGAT (middle), and co-localization of gephyrin and vGAT (bottom) in neuronal somata (gephyrin density and size: GFP, n = 22, β1-3 gRNAs, n = 24; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; vGAT density and size: GFP, n = 22, β1-3 gRNAs, n = 24, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; co-localization: percentage of gephyrin puncta colocalized with vGAT (gephyrin+ vGAT) (GFP, n = 22, β1-3 gRNAs, n = 24; ∗∗p < 0.01) and percentage of vGAT puncta colocalized with gephyrin (vGAT+ gephyrin) (GFP, n = 22, β1-3 gRNAs, n = 24; ∗∗p < 0.01); t-test; N = 5). (C) Bar graphs showed the quantitation of gephyrin (top), vGAT (middle), and co-localization of gephyrin and vGAT (bottom) in neuronal dendrites (gephyrin density and size: GFP, n = 63, β1-3 gRNAs, n = 66, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; vGAT density and size: GFP, n = 22, β1-3 gRNAs, n = 24, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗∗p < 0.01; co-localization: percentage of gephyrin puncta colocalized with vGAT (gephyrin+ vGAT) (GFP, n = 35, β1-3 gRNAs, n = 36; ∗∗p < 0.01) and percentage of vGAT puncta colocalized with gephyrin (vGAT+ gephyrin) (GFP, n = 35, β1-3 gRNAs, n = 36; ∗p < 0.05); t-test; N = 6). GFP was not immunolabeled with anti-GFP antibodies. Scale bar, 10 μm for whole cell, 5 μm for somata and dendrite. (D) Neuroligin2 (NL2) puncta were not changed in hippocampal neurons expressing β1-3 gRNAs (GFP, n = 19, β1-3 gRNAs, n = 21, p > 0.05, t-test; N = 3). GFP was immunolabeled with anti-GFP antibodies to boost the fluorescence (green). Scale bar, 5 μm. n represents the number of cells analyzed and N represents the number of independent experiments.
