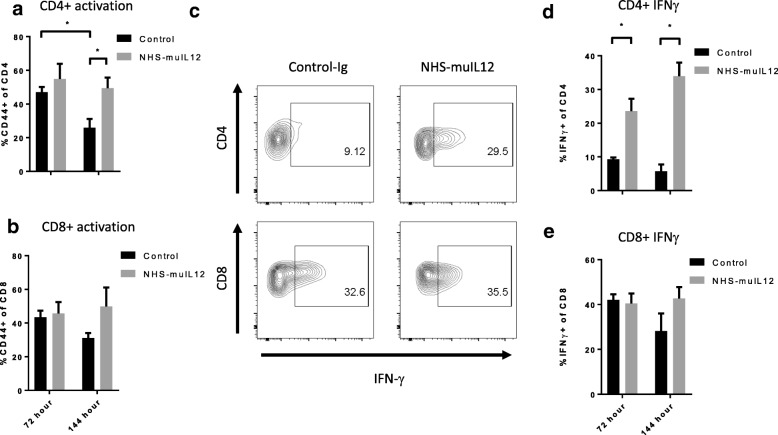
Fig. 5.
NHS-muIL12 treatment increases T cell activation (CD44 expression) and pro-inflammatory events (i.e., intracellular IFN-γ expression) within the MB49luc bladder TME. a, b MB49luc bladder tumors (n = 3) from control Ig– (black bars) and NHS-muIL12–treated (grey bars) mice were isolated at 72 and 144 h post–final NHS-muIL12 treatment and single cell suspensions were prepared (see Methods) and stained for CD4+, CD8+ T cells along with the CD44 activation marker. c Representative FACS plots for intracellular IFN-γ staining of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after a 5-h in vitro stimulation (see Methods). d, e Frequencies of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells expressing intracellular IFN-γ from MB49luc bladder tumors from control Ig– (black bars) and NHS-muIL12–treated (grey bars) mice at 72 and 144 h post–final NHS-muIL12 administration. Error bars (panels a, b, d, e) represent mean + SEM. Student’s t-test; *P < 0.05 (vs. control-treated mice)