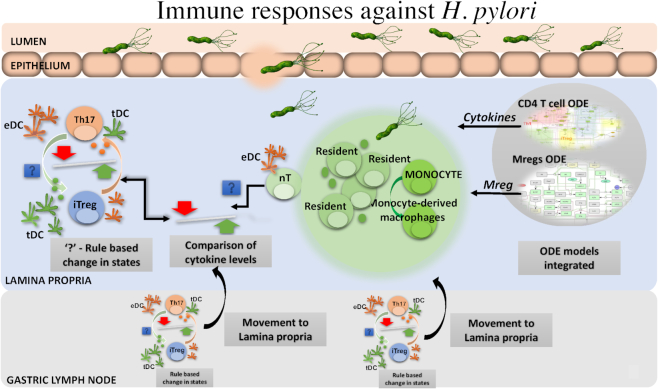
Figure 1:
Helicobacter pylori infection schematic diagram of the hybrid ABM ODE model. The model comprises of 4 compartments, (i) the lumen that contains H. pylori and bacteria; (ii) epithelium that contains epithelial cells and dendritic cells; (iii) lamina propria (LP) that contains a variety of immune cells including the infiltrating effector (eDCs) and tolerogenic dendritic cells (tDCs), monocytes, regulatory macrophages (Mreg; both resident and monocyte-derived macrophages), T helper (Th) cells, and naive CD4+ T cells (nT), Th1, iTreg, Th17, regulatory T (Treg) cells; and (iv) gastric lymph node compartment that contains eDCs, tDCs, Th1, Th17, iTreg, and nT. The Treg cells in the LP are the type 1 regulatory (Tr1) T cells with regulatory function whose expansion is largely dependent on environmental IL-10. These are different from iTreg, which are T cells differentiated from naive T cells in the presence of tDCs and TGF-β cytokines. The 2 calibrated ODEs for T cells and regulatory macrophages are integrated as the ODE components in the hybrid model. The cellular agents are simulated in a 2D grid space with their behavior defined by a set of rules during a course of H. pylori infection..