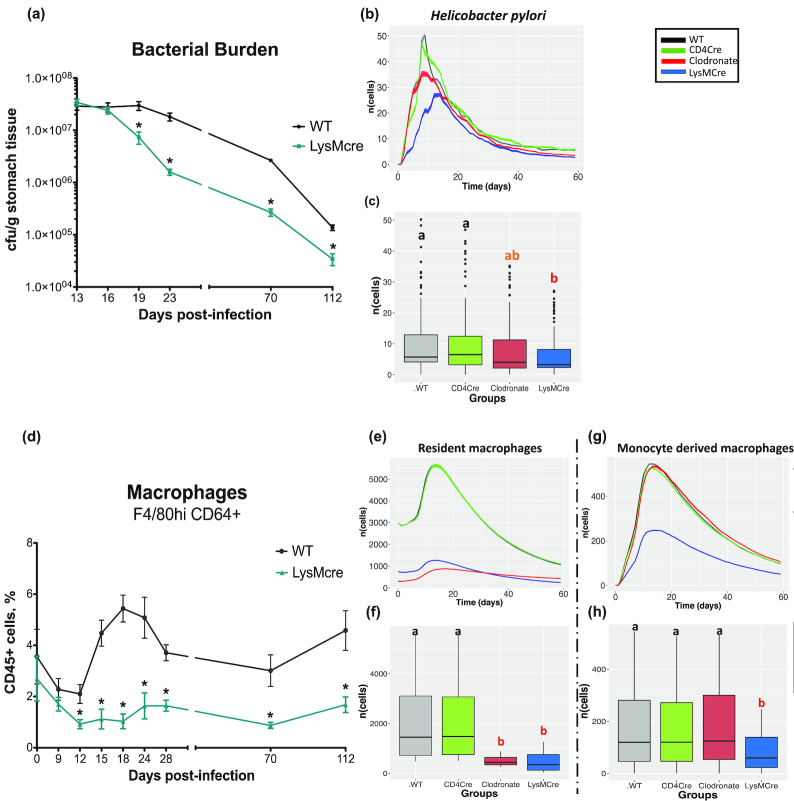
Figure 3:
Time course simulations representing the immune response during Helicobacter pylori infection. The upper half of the plot in both panels shows the dynamics of the population cells over time representing the number of cells (y-axis) vs time (x-axis) in wild type (WT) (black), CD4Cre (green), clodronate (red), and LysMCre (blue) simulated in silico groups during H. pylori infection (see Results section, Hybrid model simulations produce similar immune dynamics observed in previously published experimental datafor details about the groups). A side-by-side comparison with the bacterial load and macrophage population as observed in the mouse model of H. pylori infection is also included (a and d). The cell populations include (b) H. pylori, (e) the resident macrophages, and (g) monocyte-derived macrophages in the lamina propria compartment. The graphs in the lower half (c, f, h) of these panels show the results for statistical comparison between the groups using ANOVA with the post hoc analysis. The letters “a,” “ab,” and “b” represent statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) between the groups obtained after running the Tukey honestly significant difference. The groups with letter "a" are statistically significant different than the group with letter "b", groups with same letter are not statistically significantly different than each other. The group with letter "ab" is not statistically significantly different than group "a" and "b". In the box plots, the horizontal line is the median of the respective cell population, the box contains the interquartile range, the whiskers show the 95% confidence interval, and the dots are the outliers. cfu: colony-forming units.