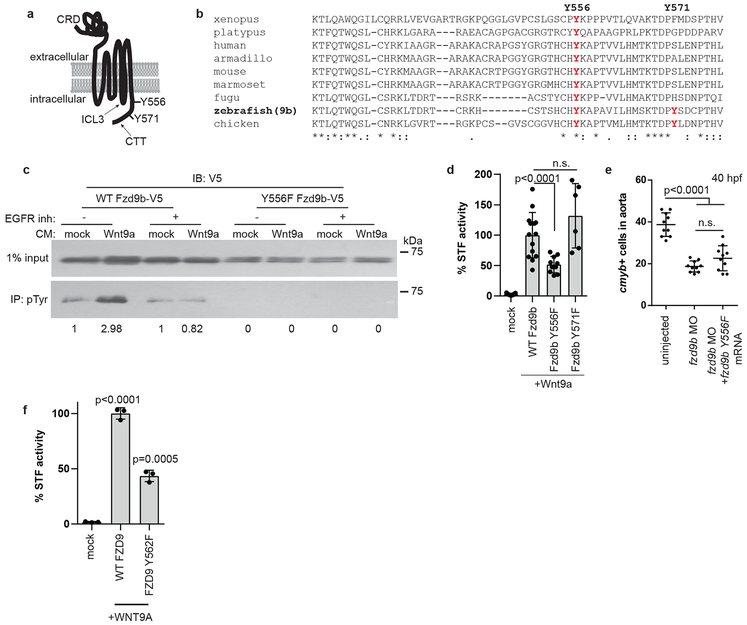
Figure 5: EGFR is required to phosphorylate the Fzd9b C-terminal tail in response to Wnt9a.
a. zFzd9b protein with putative EGFR tyrosine phosphorylation sites. CRD: cysteine rich domain, ICL3: intracellular loop 3, CTT: C-terminal tail. b. Protein alignment of Fzd9 C-terminal tails from species shown, using ClustalOmega. c. (See also Supplementary Fig. 7) Immunoblot for V5 from phosphotyrosine immunoprecipitation with increase in pY-zFzd9b (2.98 vs 1, arbitrary units). Trend observed in 4 independent experiments. d. STF assay of zFzd9b point mutants; n=9, 14, 10, 6 from left to right. e. Quantification of WISH for cmyb+ cells in uninjected, fzd9b MO injected and fzd9b MO+fzd9bY556F mRNA injected fish at 40 hpf; n=10 zebrafish each. f. Quantification of HEK293T cell STF assay with human WNT9A and FZD9 WT and Y562F mutant; n=3 biological replicates each. In all graphs, dots represent biological replicates from a single experiment; bars represent the mean and error bars represent the standard deviation. n.s. not significant. Statistical analyses by ANOVA compared to control as indicated. All STF assays were repeated independently with a similar trend.