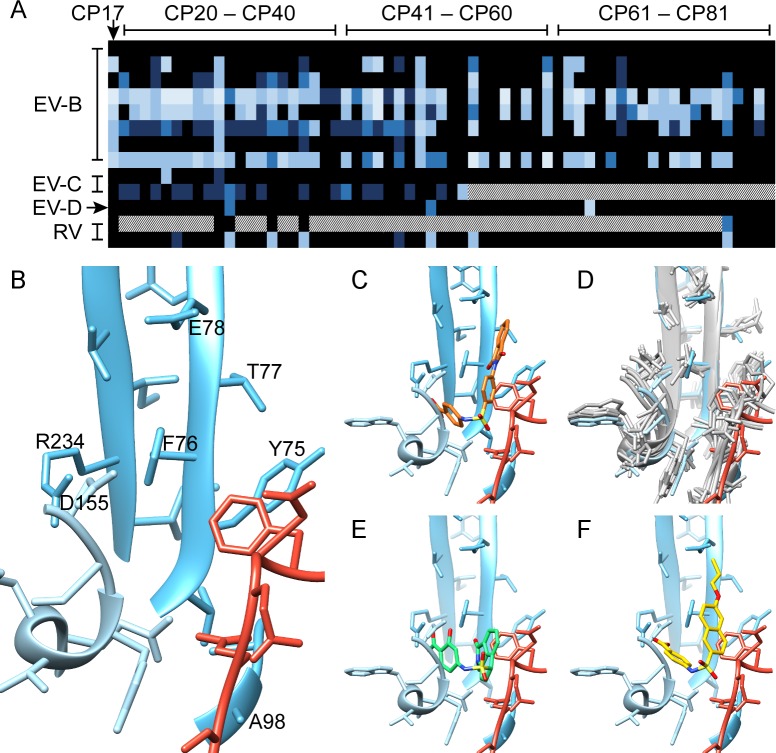
Fig 3. Discovery of new CP17 analogues with improved potency and spectrum.
(A) Heat map of the activity (EC50) of CP17 and the 62 analogues (CP20–CP81) in the context of EV-B (CVB1, CVB2, CVB3, CVB3_L92I, CVB4, CVB5, and CVB6), EV-C (CVA21 and PV1), EV-D (EVD68), and RV (RVA63 and RVB14) infection. Color range: black (inactive compounds)–light blue (compounds with EC50 < 1 μM). For white-dotted pixels, EC50 was not determined. EC50 values and compounds structures are available in S1 Table. (B) Pocket residues of VP1 proteins (blue, light blue) and VP3 (red), with those labelled that, when mutated, induced resistance to compound 17. (C) Position of compound 17 in the pocket (orange). (D) Pocket structural conservation for related enteroviruses exhibiting sensitivity to compound 17: an overlay of the solved structure (blue/light blue/red) with atomic models (gray) of CVB3 (wwPDB ID:1COV), CVA9 (wwPDB ID:1D4M), EVD68 (wwPDB ID:4WM8), E1 (wwPDB ID:1EV1), E7 (wwPDB ID:2X5I), and E11 (wwPDB ID:1H8T). RMSD statistics found in S4 Table. (E) The predicted docking of compound 29 (green) into the solved structure. (F) The predicted docking of compound 48 (yellow). CP17, compound 17; CVA, Coxsackievirus A; CVB, Coxsackievirus B; E, echovirus; EC50, 50% effective concentration; EV-B, enterovirus-B; EV-C, enterovirus-C; EV-D, enterovirus-D; EVD68, enterovirus D68; PV, poliovirus; RMSD, root mean square deviation; RV, rhinovirus; RVA63, rhinovirus A63; RVB14, rhinovirus B14; ww, worldwide.