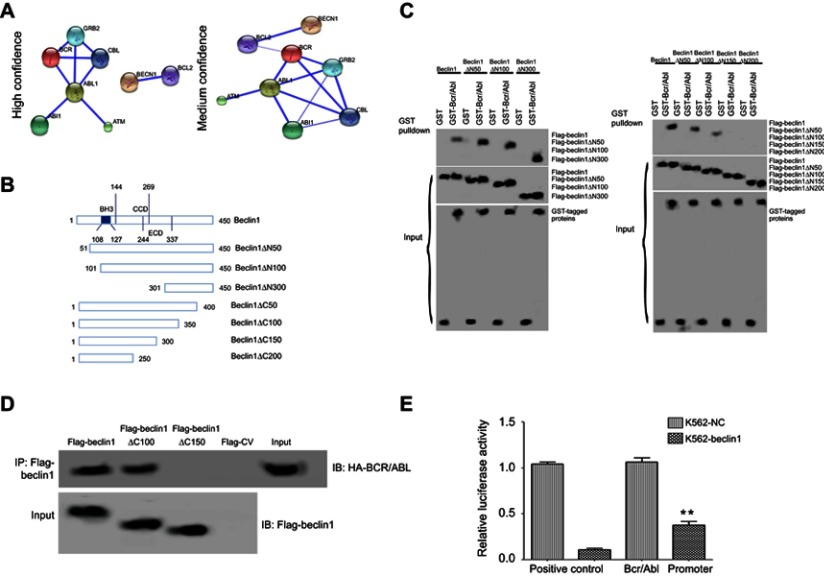
Figure 1.
The interaction between BCR/ABL and Beclin1. (A) Prediction of the interaction between Beclin1 and BCR/ABL using bioinformatics analysis. (B) Schematic structures of the Beclin1 mutant constructs, which were generated using a PCR-based mutagenesis method. (C) The BCR/ABL-binding motifs in Beclin1 were evaluated using Flag-Beclin1 and the deletion mutant constructs, which were cotransfected into HEK 293T cells with GST or GST-tagged BCR/ABL. The interactions between the proteins were determined via GST pull-down assays. (D) K562 cells electrotransfected with the indicated plasmids were subjected to immunoprecipitation with an anti- Flag antibody. The immunoprecipitated complexes were separated via SDS-PAGE and probed with an anti- Flag antibody to detect Flag-tagged Beclin1 and the mutant constructs and an anti-HA antibody to detect HA-tagged BCR/ABL. (E) K562-Beclin1 or K562-NC cells were electrotransfected with the pRL-TK and pGL3-BCR/ABL promoter constructs. The dual-luciferase reporter assay revealed the binding of Beclin1 to the BCR/ABL promoter in K562 cells. The results are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD); **P<0.01. Data are representative of three independent experiments.
Abbreviation: NC, negative control.