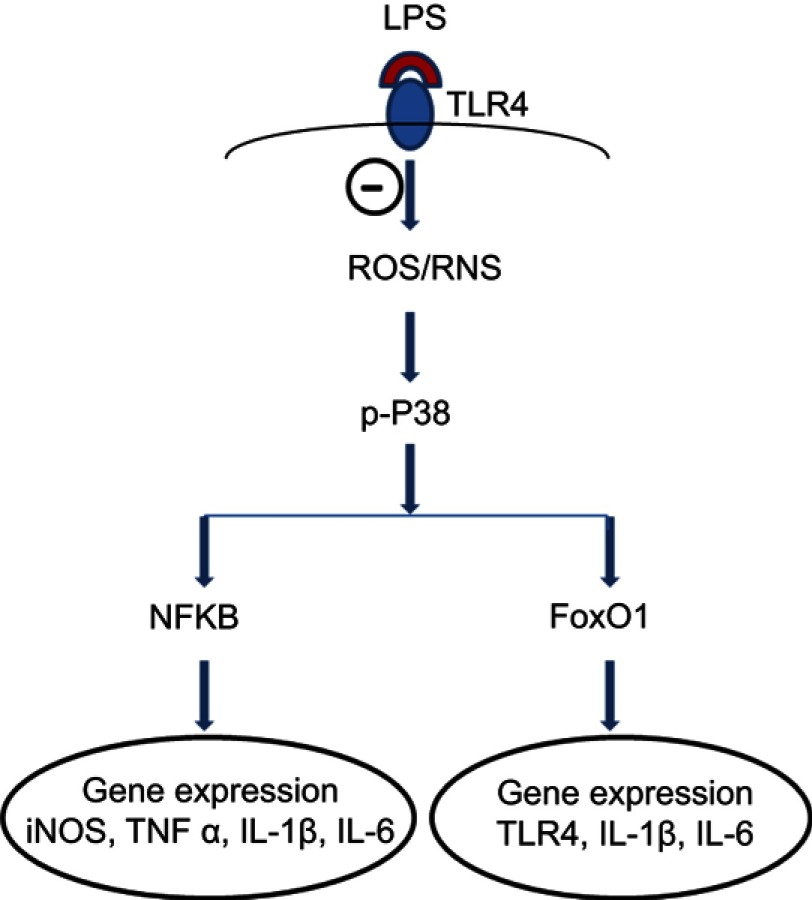
Figure 7.
A proposed mechanism underlying inhibitory effects of fullerol on inflammation-related gene expression in LPS-activated macrophages. The symbol ⊝ represents inhibition of fullerol against free radicals produced after binding of LPS to its ligand TLR4. The p38 MAPK plays a pivotal role in the regulation. Through transcription factors, NFkB and FoxO1, the expression of targeted genes was regulated. The decrease in iNOS and TLR4 expression reduces the cellular level of reactive nitrogen species (RNS) and TLR4 protein, which further minimizes the inflammatory effects of LPS. It is worth noting that other signal pathways might also be involved in the anti-inflammation of fullerol.
Abbreviations: FoxO1, forkhead box transcription factor 1; iNOS, induced nitric oxide synthase; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NFkB, nuclear factor-kappaB; TLR, toll-like receptor.