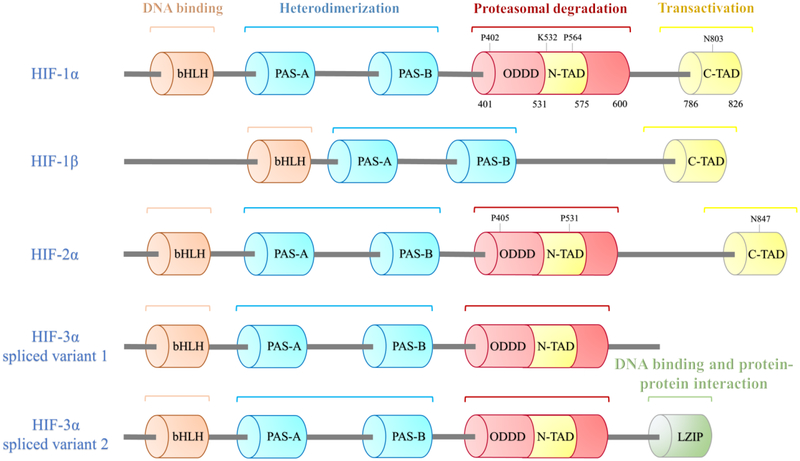
Figure 1.
Functional domain structures of HIF isoforms and their potential function. Columns represent different function domains. The hydroxylation sites are shown above the domain. HIF isoforms are bHLH–PAS proteins, they all have a bHLH motif, two PAS domains (PAS-A and PAS-B) for the heterodimerization between HIF-α and HIF-1β. Unlike HIF-1β, HIF-α subunits have an ODDD that mediates hydroxylation of two proline (P) residues and the acetylation of a lysine (K) followed by proteasomal degradation, a N-TAD within the ODDD and a C-TAD, which involved in transcriptional activation. The proline residues are conserved in HIF-1/2α subunits. Multiple HIF-3α splice variants exist, such as HIF-3α variant 1 without C-TAD and HIF-3α variant 2 with a LZIP, which mediates DNA binding and protein-protein interaction.