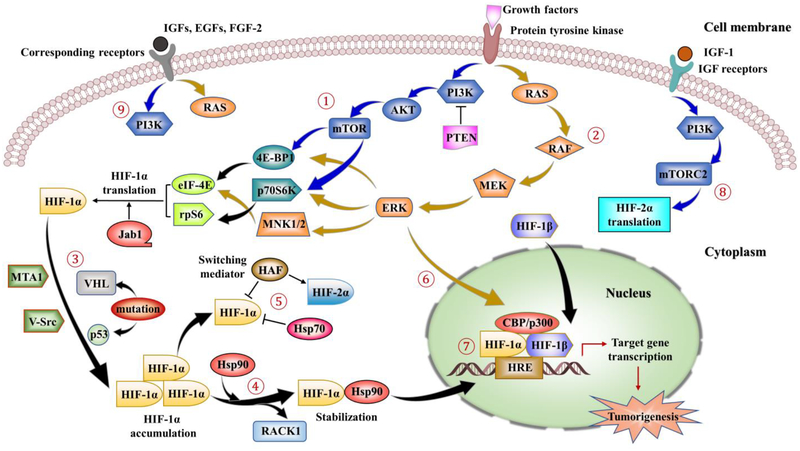
Figure 3.
Main signaling involved in non-canonical pathways regulating HIF-1/2. ①-②: HIF-1α regulation could be initiated by growth factors stimulation via activation of protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs). This stimulation leads to downstream signaling activations via the PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathway (indicated by the blue arrows) and MAPK/ERK pathway (indicated by dark yellow arrows). mTOR and ERK signaling further mediate phosphorylation and activation of three downstream effectors, 4E-BP1, p70S6K and MNK1/2, followed by the activation of eIF-4E and rpS6. Finally, these phosphorylation actions result in enhanced translation of HIF-1α mRNA into protein. In addition, Jab1 may promote the transcriptional activity of HIF-1α, while PTEN, a negative regulator of the PI3K, could downregulate the HIF-1α expression. ③: Mutations of VHL, PTEN and p53 result in increased expression of HIF-1α, as well as activations of oncogenes, such as MTA1 and V-Src. ④: Hsp90 competes with the RACK1 for binding to the HIF-1α PAS domain since RACK1 destabilizes HIF-1α via proteasomal degradation pathway. HIF-1α further accumulates in the cytoplasm with the help of Hsp90 which assists the protein folding, prevents the degradation of HIF-1α by the proteasome and contributes its nuclear translocation. ⑤: HIF-1α is also regulated by HAF by inducing the degradation of HIF-1α, while increasing HIF-2α transactivation. Compared with Hsp90, Hsp70 could mediate HIF-1α degradation in the prolonged hypoxia but not HIF-2α. ⑥: ERK phosphorylates the co-activator CBP/p300 and increases HIF-1α/p300 complex formation. ⑦: In the nucleus, the HIF complex binds to the HREs motif on the DNA of target genes and activates the transcription, causing the upregulation of genes involved in cell proliferation, cell survival, angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. ⑧: IGF-1 activation could induce the transcription of HIF-2α via PI3K-mTORC2 system. ⑨: Stimulations of IGFs, EGFs and FGF-2 on corresponding receptors induce HIF-1α expression and protein synthesis through activation of both PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways.